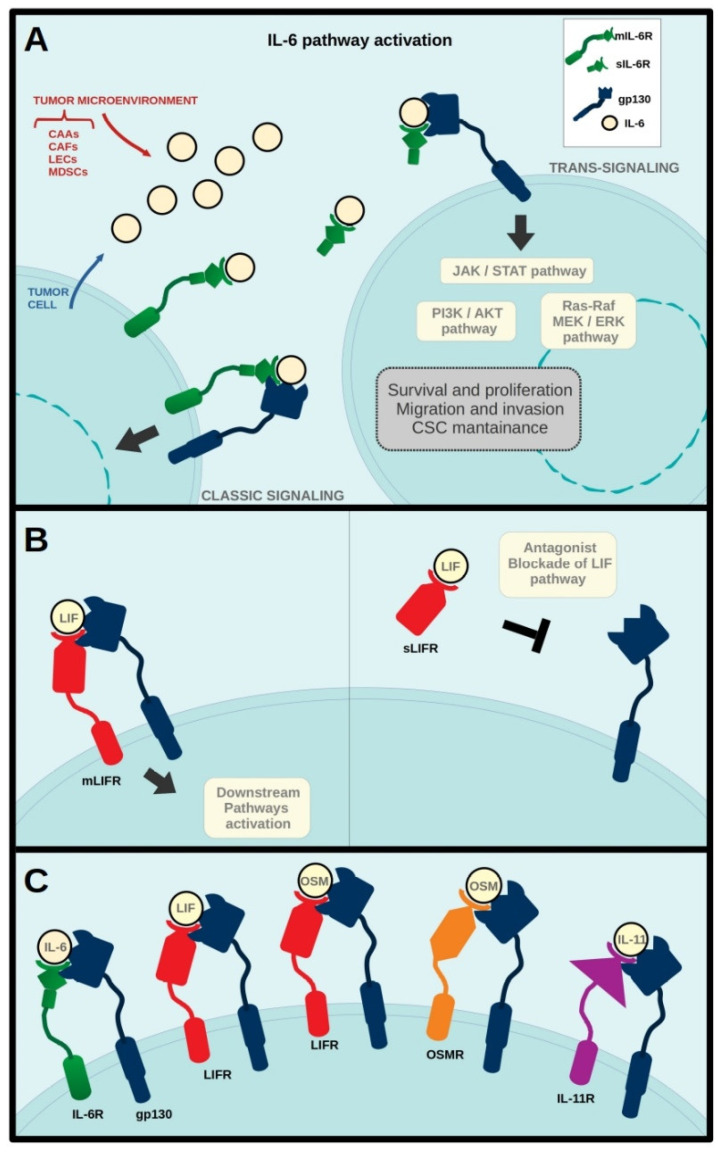
Figure 1.
IL-6 cytokine pathway activation in breast cancer cells. IL-6 is secreted by tumor and stroma cells, such as cancer associated adipocytes (CAAs), cancer associated fibroblasts (CAFs), lymphatic endothelial cells (LECs), and myeloid derived stem cells (MDSCs). IL-6 binds to either transmembrane (mIL-6R) or soluble (sIL-6R) IL-6 receptor and to gp130 inducing ‘classic signaling’ through mIL-6R or ‘trans-signaling’ through sIL-6R (A). LIF binds to transmembrane LIF receptor (mLIFR) and gp130 inducing downstream signaling. LIF binding to soluble LIF receptors (sLIFR) blocks interaction with gp130 inhibiting LIF pathway activation (B). At the surface of target cells, secreted IL-6 cytokine family members bind to their specific receptors and gp130 to activate intracellular signaling cascades (C).