Figure 3.
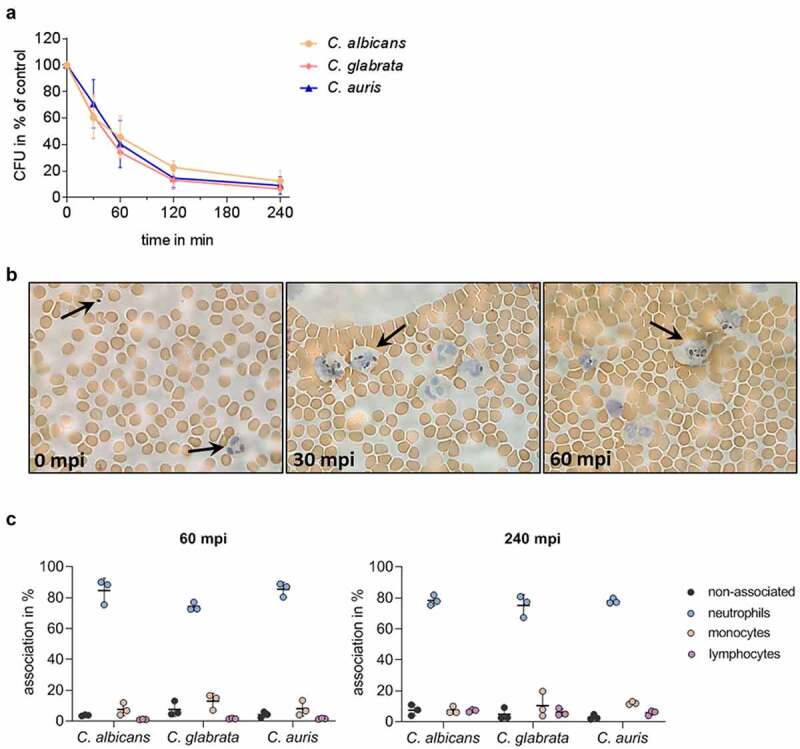
C. auris interacts with immune cells and is efficiently killed during ex vivo whole blood infection. (a) Survival of C. auris, C. albicans, and C. glabrata in human whole blood was determined 30, 60, 120, and 240 minutes post infection (mpi) by CFU quantification relative to time point 0 mpi as 100%. n = 6, mean ± SD (b) Exemplary microscopic pictures of blood smears prepared at indicated time points from C. auris infected whole blood. Arrows indicate fungal and human immune cells. 100 x magnification (c) Association of fungal cells with immune cells was determined by fluorescence activated cell sorting (FACS) analyses at 60 mpi and 240 mpi. n = 3, mean ± SD for independent experiments using different donors.
