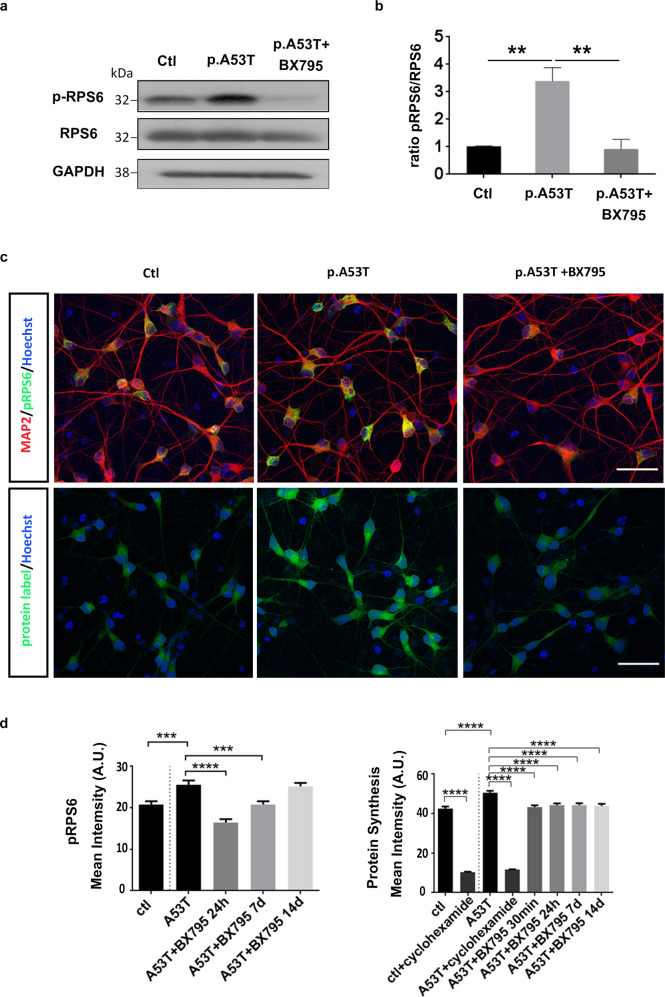
Fig. 7. BX795 affects the mTORC1 signaling pathway in p.A53T patient-derived and iCell Dopa neurons to attenuate protein synthesis.
a Western blot showing increased levels of p-RPS6 in p.A53T-patient iPSC-derived neurons and a notable reduction in the presence of BX795. GADPH shows equal protein. b Quantification of p-RPS6 levels in p.A53T-patient iPS-derived neurons. Data represent mean ± SEM (Comparisons by ANOVA with Bonferroni’s multiple comparisons test. **P < 0.01, n = 3 independent experiments). c Representative confocal images of control (ctl) and isogenic gene-edited p.A53T iCellDopa neurons, either non-treated or treated with BX795. Cells were immunolabeled for phosphorylated RPS6 (green) andmicrotubule associated protein 2 (MAP2; red)(upper panel) and labeled for total protein synthesis (protein label, green)(lower panel). Nuclei are seen with Hoechst dye (blue). Scale bar, 30 μm. d BX795 reduces phosphorylated RPS6 levels and reduces total protein synthesis in p.A53T-neurons. Quantification of fluorescence intensity in control, untreated p.A53T or BX795-treated p.A53T neurons. Data represent mean ± SEM (Comparisons by ANOVA with Tukey correction, ***P < 0.001 ****P < 0.0001, n = 100 randomly selected cells for each condition).