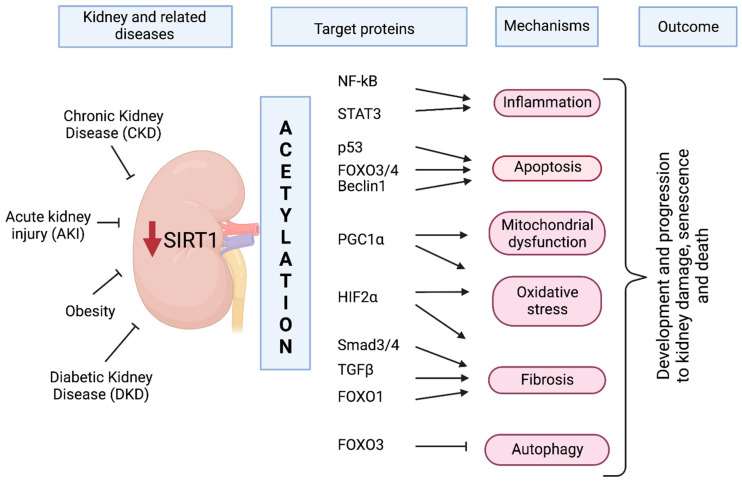
Figure 1.
Dysregulation of SIRT1 in kidney-related diseases and the target proteins involved. SIRT1 deacetylase activity and expression are reduced (red arrow), which increases acetylation/activation of several transcription factors, leading to aggravated effects, such as inflammation, apoptosis, fibrosis, oxidative stress, and autophagy dysfunction in kidney tissue. Together, these processes contribute to the development and progression of kidney-related disorders. Therefore, the main role of SIRT1 is to protect the kidney by preserving renal homeostasis. Stimulation, ➜; inhibition, ⟞; red down arrow.