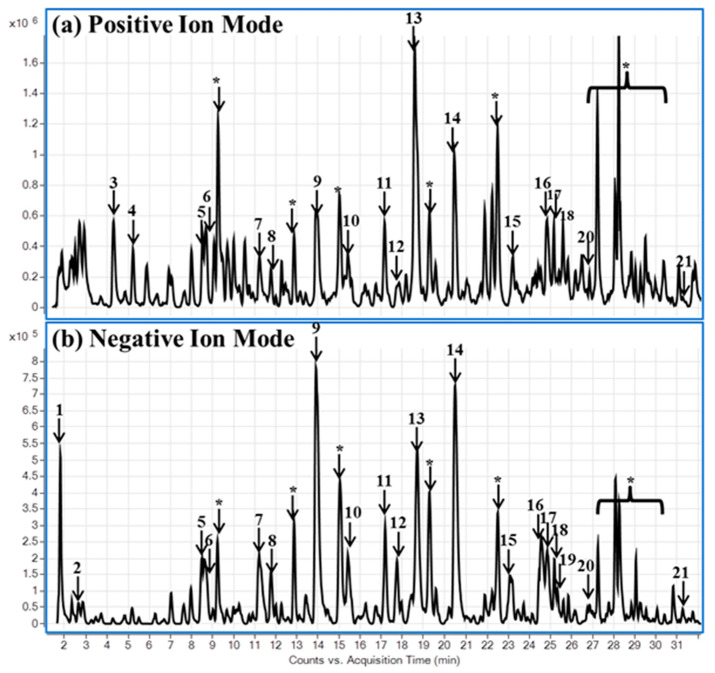
Figure 4.
Phytochemical analysis of A. sinensis flower extract. LC-QToF base peak chromatograms are shown in (a) positive and (b) negative ion modes. The tentatively identified compounds are (1) malic acid; (2) succinic acid; (3) phenylalanine; (4) procatechuic acid; (5) iriflophenone 3-C-glucoside; (6) iriflophenone 3,5-di-C-β-D-glucopyranoside; (7–8) mangiferin/isomangiferin; (9) iriflophenone 2-rhamnoside; (10–13) iriflophenone 2-O-α-L-(4″-acetyl)-rhamnopyranoside/aquilarinenoside E; (14) kaempferol-3-O-β-D-glucopyranoside; (15) kaempferol diglucoside; (16) aquilarisinine; (17–18) kaempferol (p-coumaroyl-glucoside)/ kaempferol (p-coumaroyl-galactoside); (19) isorhamnetin coumarylglucoside; (20) kaempferol; (21) genkwanin; (*) unknown compounds.