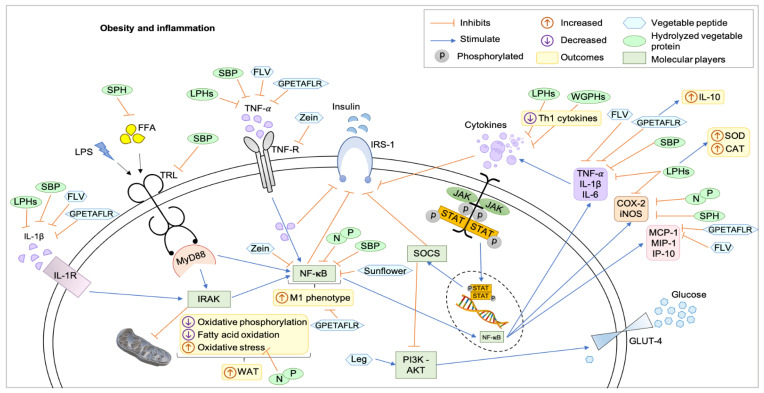
Figure 1.
Mechanisms of action of hydrolyzed proteins and plant peptides on obesity and inflammation in a hypothetical eukaryotic cell. All hydrolyzed proteins and peptides acted to reduce inflammation through metabolic pathways that communicate and are responsible for the positive feedback cascade for the accumulation of more adipose tissue and subclinical inflammation, as well as some compounds acted by feeding detoxification and detoxification pathways. reduction of oxidative stress. CAT: catalase, COX-2: cyclooxygenase-2, FFA: free fatty acid, FLV: soy peptide Phe–Leu–Val, GLUT4: glucose transporter type 4, GPETAFLR: peptide from Lupinus angustifolius L., IL-10: interleukins-10, IL-6: interleukins-6, IL1-β: interleukins-1β, IL1-R: interleukins-1-receptor, iNOS: inducible nitric oxide synthase, IP-10: interferon-inducible protein 10, IRAK: IL-1R-associated kinase 2, IRS-1: insulin receptor substrate 1, JAK-STAT: Janus kinase—signal transducer and activator of transcription, Leg: Leginsulin, LPHs: lupine protein hydrolysates, LPS: lipopolysaccharides, M1: M1-like macrophage, MCP-1: monocyte chemoattractant protein-1, MIP-1: macrophage inflammatory protein-1, MyD88: myeloid differentiation primary response 88, N and P: protein hydrolysates of the common bean (Phaseolus vulgaris L.) varieties Negro 8025 and Pinto Durango, NFκB: factor nuclear kappa B, PI3K-AKT: phosphatidylinositol 3-kinase/protein kinase B, SBP: soybean protein-derived peptides, SOCS: suppressor of cytokine signaling, SOD: superoxide dismutase, SPH: soy protein peptic hydrolysate, sunflower: peptides from sunflower protein hydrolysate, Th1: T helper 1, TNF-α: tumor necrosis factor-α, TNF-R: tumor necrosis factor-receptor, TRL: toll-like receptor, WAT: white adipose tissue, WGPHs: wheat gluten protein hydrolysates, zein: peptides for zein hydrolysate.