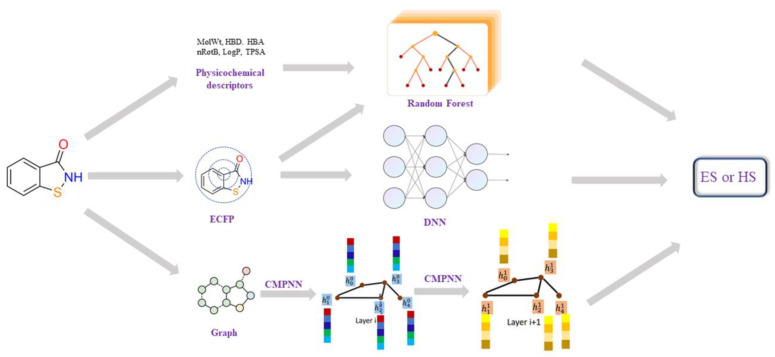
Figure 5.
The workflow of different synthesis accessibility prediction models, including: (1) Random Forest model using the physicochemical descriptors; (2) DNN models using ECFP4; (3) graph convolution neural-network-based model using molecular 2D graph structure. Each node (atom) of a graph (molecule) is represented by a feature vector of 133 dimensions, including ‘atomic number’, ‘degree’, ‘formal charge’, ‘number of hydrogens’, ‘hybridization’ and ‘chiral tag’. Then, these node features, together with edge (bond) information, are processed by a Communicative Message Passing Neural Network (CMPNN) to generate a molecular feature.