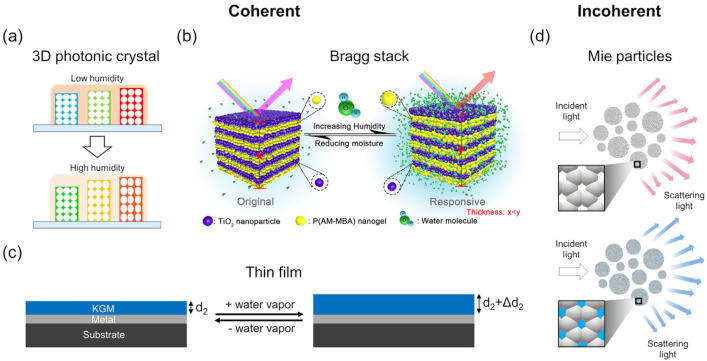
Figure 10.
Schematic illustrating humidity-responsive structural colors from coherent (a–c) and incoherent (d) light interference. (a) A 3D photonic crystal composed of an inverse opal photonic gel in hydrophilic ionic liquid that swells and shrinks in response to humidity [92]. Courtesy: Adapted with permission from ref. [92]. Copyright 2018 MDPI. (b) Mesoporous 1D photonic crystal or Bragg stack, composed of alternating layers of nanogels and TiO2 nanoparticles [93]. Courtesy: Adapted with permission from ref. [93]. Copyright 2018 American Chemical Society. (c) A thin-film assembly of konjac glucomannan (KGM)–metal–substrate humidity sensor and KGM thickness changes as a result of humidity-induced swelling and shrinking [100]. Courtesy: Adapted with permission from ref. [100]. Copyright 2020 American Chemical Society. (d) Disordered assembly of mesoporous titania microspheres showing changes in scattered colors in response to humidity. The insets show models of the porous network inside the titania microsphere under dry (top) and humid (bottom) conditions [110]. Courtesy: Adapted with permission from ref. [110]. Copyright 2021 Royal Society of Chemistry.