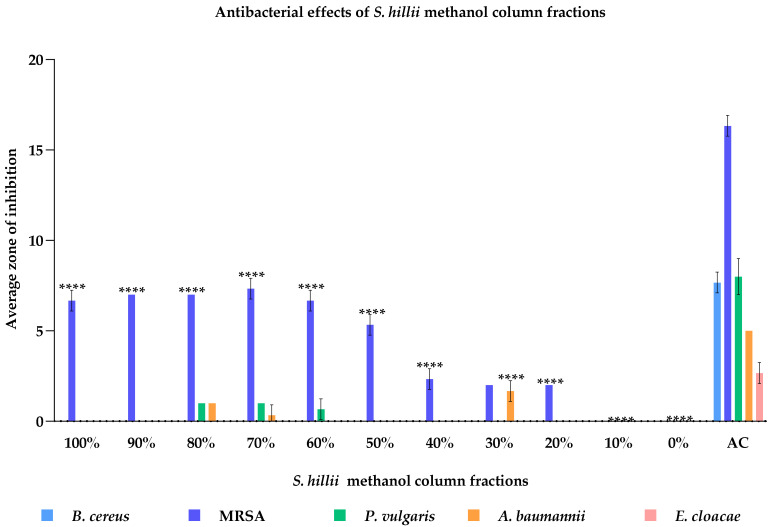
Figure 2.
Antibacterial effects of S. hillii column fractions against B. cereus, MRSA, P. vulgaris, A. baumannii, and E. cloacae at 10 mg/mL. B. cereus (ATCC 14579) was resistant to all methanol fractions at the tested concentration. 20–100% fractions showed antibacterial effects against MRSA (ATCC 33591). The 30% fraction elicited the highest antibacterial effects against A. baumannii (ATCC 19606). However, the antibacterial activities of all the fractions were significantly low compared to the antibiotic standards (p < 0.0001). Eleven fractions were tested against five bacterial species, which were shown to be susceptible to the S. hillii methanol extract in the preliminary antibacterial screening. ZOI (zone of inhibition) was measured using the radius from the edge of the well to the edge of the clear zone (mm) and are expressed as the mean of triplicates ± standard error (SEM). Significance levels **** p < 0.0001 compared to antibiotic control (AC). MRSA: methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus. AC: antibiotic control.