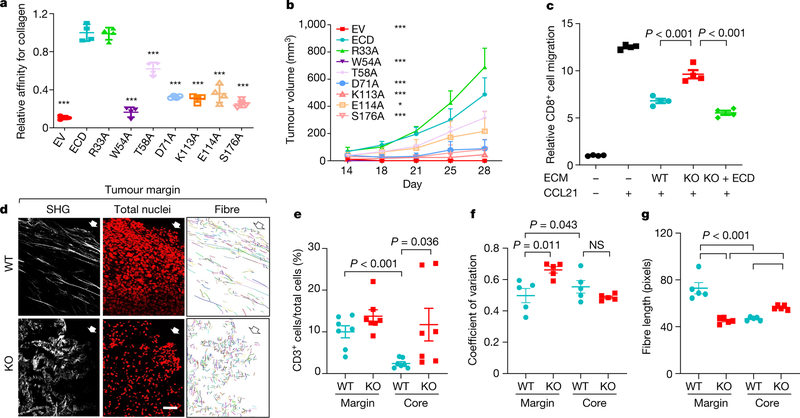
Fig. 3 |. DDR1-dependent ECM remodelling inhibits anti-tumour immune infiltration.
a, ELISA of collagen binding of wild-type and mutant DDR1-ECD from E0771 Ddr1-KO cells (n = 4 technical repeats). Three biological repeats. All P values were compared to the wild-type ECD. ***P < 0.001. EV, empty vector. b, Growth of E0771 Ddr1-KO tumour cells with empty vector, ECD WT or point mutants (KO + EV, n = 8 tumours; KO + WT ECD, n = 10 tumours; KO + mutant ECD, n = 6 tumours). All P values were compared to the wild-type ECD group. *P < 0.05, ***P < 0.001. c, Decellularized ECM from E0771 tumour cells inhibits T cell migration. Value of migrated CD8+ T cell number without ECM and CCL12 is set at ‘1’ (n = 4 technical repeats). Three biological repeats. d, E0771 tumours transplanted from Rag1−/− to C57BL/6 hosts were analysed by SHG, To-pro-3 staining for all nuclei, and collagen fibre individualization. Block arrows indicate tumour margins. Scale bar, 50 μm. e, Quantification of CD3+ T cells by IHC (WT, n = 7 tumours; KO, n = 7 tumours). f, g, Tumour fibre alignment (f) and fibre length (g) by the CT-Fire software (n = 5 tumours per group). Values represent mean ± s.e.m. P values as indicated; NS, not significant; two-tailed Student’s t-test for all tests except for tumour volumes (two-way ANOVA).