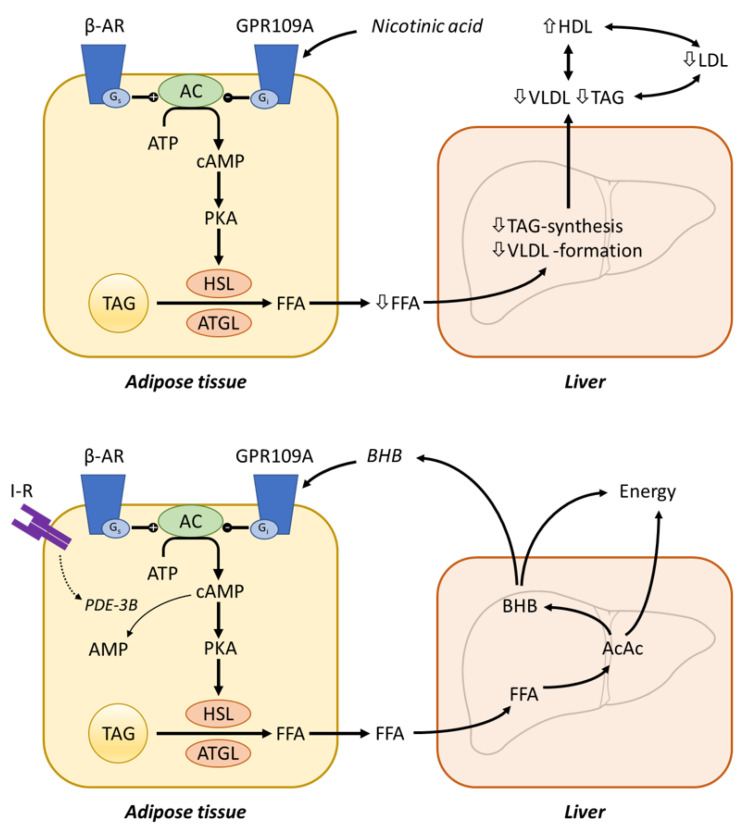
Figure 12.
GPR109A receptor function. (upper panel) Metabolic effects of nicotinic acid. Activation of nicotinic acid receptor inhibits the mobilization of free fatty acids (FFA) from adipocytes and lowers the production of VLDL in hepatocytes with consequently decreased plasma levels of VLDL/LDL. TAG inhibit the cholesterol transfer to HDL via cholesteryl ester transfer protein (CETP). (bottom panel) Possible physiological role of GPR109A. In fasting, increased activity of the sympathetic nervous system and low insulin levels stimulate breakdown of TAG into FFA. Hepatic metabolism produces β-hydroxybutyrate (BHB) and acetoacetate (AcAc) as energy sources. BHB forms a negative feedback loop that limits the fat catabolism in adipose tissue.