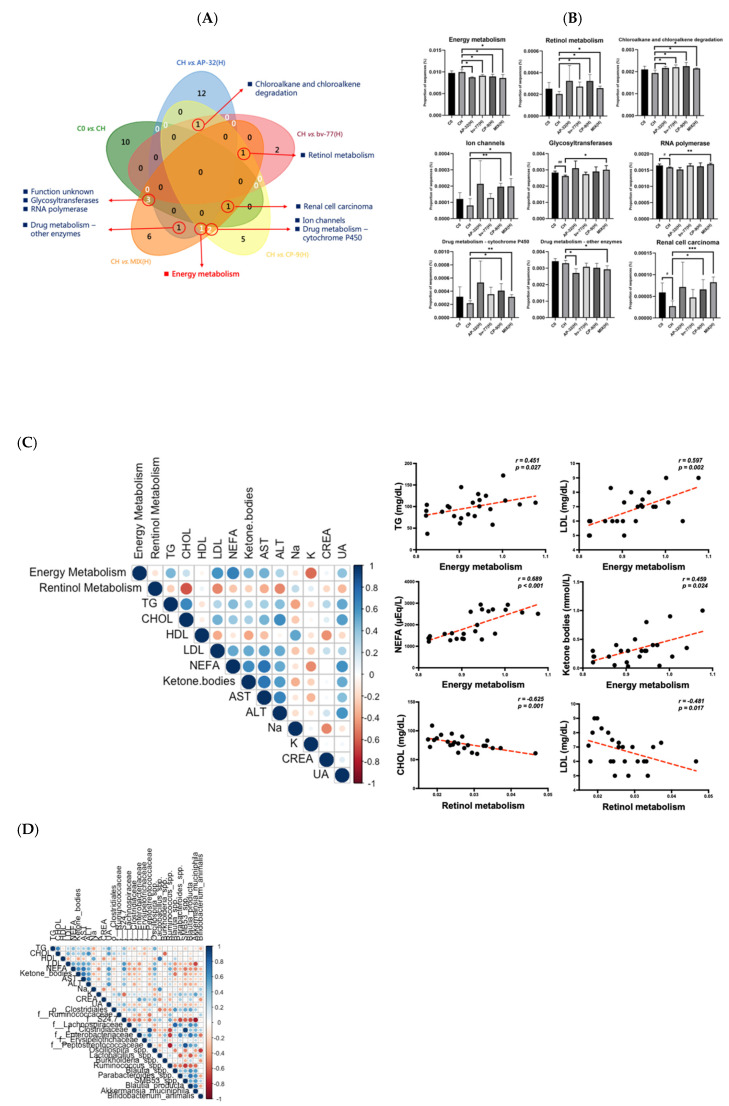
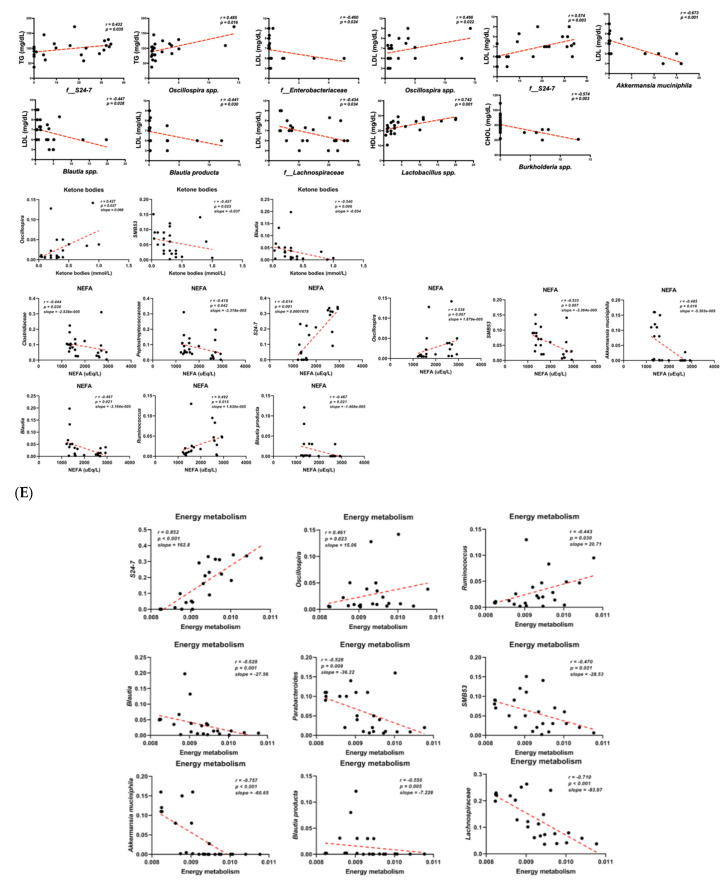
Figure 6.
Functional pathways modulated by gut microbiota and association. A total of nine key functional pathways were found to be associated with the probiotic treatments. (A) Venn plot of functional pathways affected by changes in gut microbiota. (B) Bar graph showing the nine functional pathways responsive to the probiotic treatments. (C) Spearman’s correlation heatmap displayed the relationship of blood biochemistry with energy metabolism and retinol metabolism. Scatter plots displayed the energy metabolism was positively correlated with NEFA, ketone bodies, TG, and LDL. Retinol metabolism was negatively correlated with CHOL and LDL. (D) Spearman’s correlation heatmap displaying the relationship of blood biochemistry with gut microbiota. Scatter plots displaying that ketone bodies were positively correlated with Oscillospira and negatively correlated with SMB53 and Blautia. NEFAs were positively correlated with Oscillospira, S24-7, and Ruminococcus, and negatively correlated with SMB53, Blautia, Clostridaceae, Peptostreptococcaceae, and A. muciniphila. (E) Scatter plots displaying that energy metabolism was positively correlated with S24-7, Oscillospira, and Ruminococcus. In constant, it was negatively correlated with Lachnospiraceae, SMB53, Blautia, Parabacteroides, and A. muciniphila. Statistical analyses were performed by using the Student’s t-test. Statistical difference is shown as comparison between the CH and probiotics-treated groups (# p < 0.05, ## p < 0.01; * p < 0.05, ** p < 0.01, *** p < 0.001).