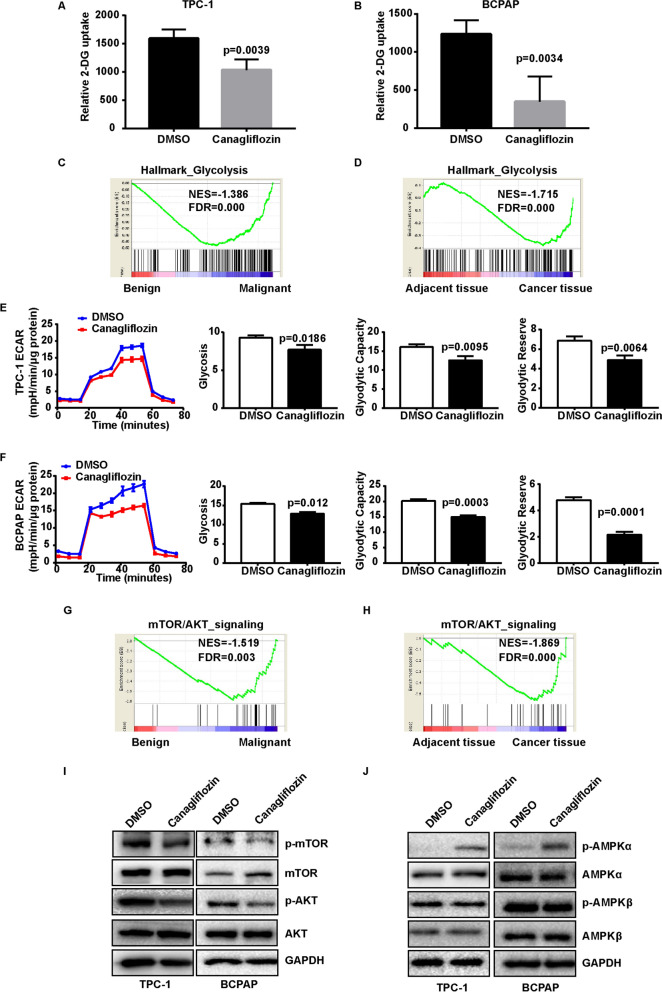
Fig. 2.
The effect of canagliflozin on glucose uptake and glycolysis of TPC-1 and BCPAP cells. A, B Canagliflozin inhibited 2-DG uptake in TPC-1 and BCPAP cells TPC-1 and BCPAP cells were treated with 10 μM canagliflozin for 24 h, and 2-DG uptake were measured by Glucose Uptake Assay Kit. A t-TEST was used to determine statistical significance. C Gene signatures for glycolysis were enriched in malignant thyroid cancer in patients. D Gene signatures for glycolysis were enriched in thyroid cancer tissue in TCGA dataset. E, F Canagliflozin inhibited glycolysis level in TPC-1 and BCPAP cells. TPC-1 and BCPAP cells were treated with 10 μM canagliflozin for 24 h, then the ECAR were monitored in baseline conditions and treated with 10 mM glucose, 1 µM oligomycin, and 50 mM 2- DG. Cells were collected in 100 μL lysis, and detected protein concentration by BCA kit. The date were analyzied by Seahorse XF-Glycolysis Stress Test. The ECAR were normalized by the protein quantification. G Gene signatures for AKT/mTOR activation were enriched in malignant thyroid cancer in patients. H Gene signatures for AKT/mTOR activation were enriched in thyroid cancer tissue in TCGA dataset. I, J Canagliflozin reduced the phosphorylation of AKT and mTOR and increased the phosphorylation of AMPK. Cells were treated with 10 μM canagliflozin for 24 h, then the cells were collected, p-AKT, AKT, p-mTOR, mTOR, p-AMPKα, AMPKα, p-AMPKβ, and AMPKβ were detected by western blot. GAPDH was used as a loading control