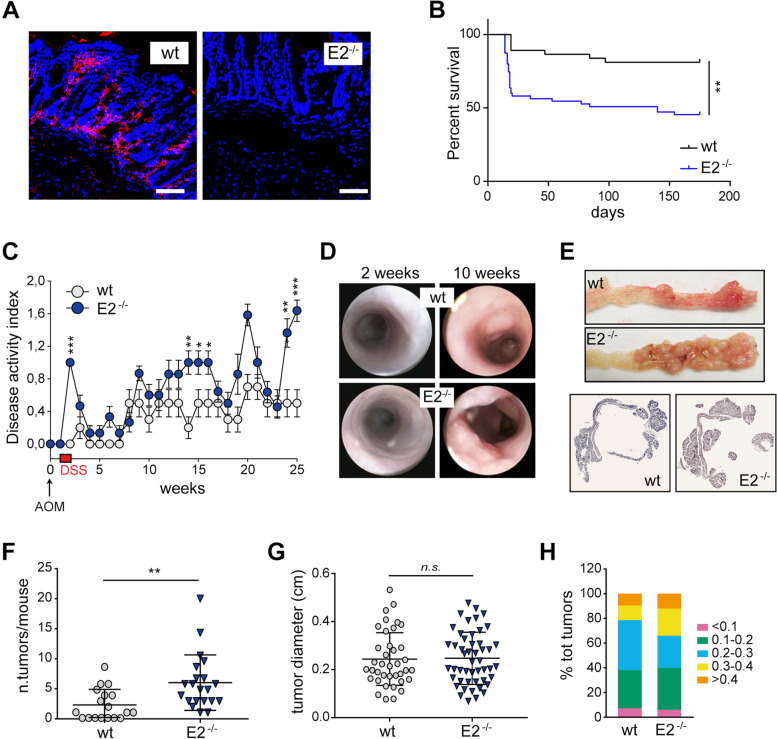
Fig. 2.
Ablation of EMILIN-2 associates with exacerbated tumorigenesis upon AOM/DSS treatment in mice. A EMILIN-2 staining in the colonic mucosa of wild type (wt) and Emilin-2−/− (E2−/−) mice; Blue: nuclei; red: EMILIN-2; scale bar = 50 μm. B Kaplan-Meier graph showing the overall survival of wild type (wt; n = 30) and Emilin-2−/− (E2−/−; n = 50) mice treated with AOM/DSS. Log-rank test, P = 0,0025. C Graph showing the Disease Activity Index (DAI) assessed in wild type (wt; n = 18) and Emilin-2−/− (E2−/−; n = 21) mice during AOM/DSS treatment. D Endoscopic images of the colonic mucosa of wild type (wt) and Emilin-2−/− (E2−/−) mice at 2 and 10 weeks from the AOM administration. E Top, macroscopic images of the tumors developed in wild type (wt) and Emilin-2−/− (E2−/−) mice 25 weeks after AOM administration; bottom, H&E staining of the colon sections from the experiment reported in E. F Graph indicating the number of tumors per mouse developed in wild type (wt; n = 18) and Emilin-2−/− (E2−/−; n = 21) animals upon AOM/DSS induced CRC; each dot represents a single animal. G Graph showing the diameter of the colon lesions developed in wild type (wt) and Emilin-2−/− (E2−/−) mice; each dot represents a single tumor. H Evaluation of the tumor diameter of the CRC lesions developed in wild type (wt) and Emilin-2−/− (E2−/−) mice. Graphs in C, F and g represent the mean ± SD; P values were obtained using the paired Student’s t-test; **P < 0.01, ***P < 0.001, n.s.: P > 0.05