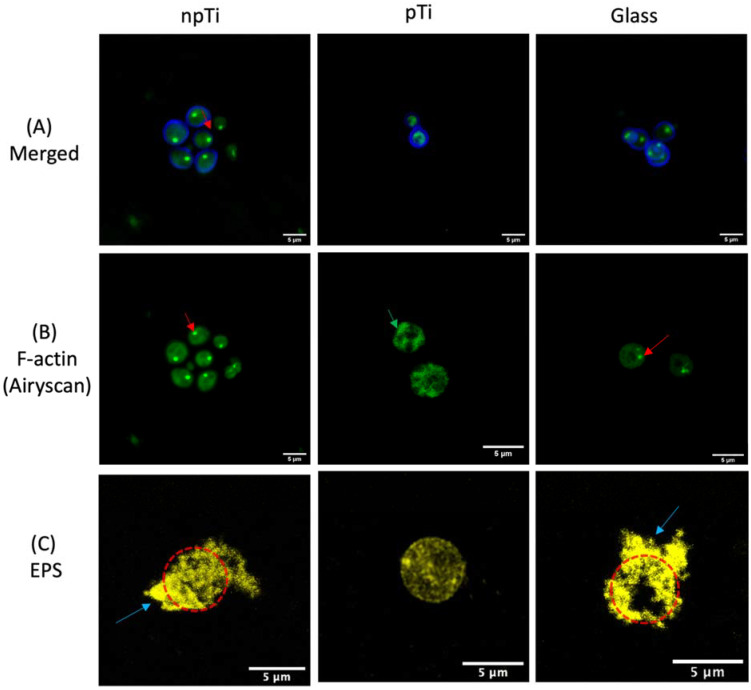
Figure 4.
Cell wall, F-actin staining, and EPS production of C. albicans attached on npTi, pTi, and glass surfaces after a 3-day incubation period. (A) CLSM micrographs of C. albicans cells stained with calcofluor white (blue color) and phalloidin, which selectively stains F-actin (green color). (B) High-resolution CLSM (Airyscan) micrographs of filamentous actin distribution of C. albicans cells on the three studied surfaces. The red arrow indicates representative actin patches. The green arrow shows the lack of actin patches and the condenses in F-actin distribution of attached cells on pTi. (C) C. albicans cells were stained with Concanavalin A, which specifically binds to the a-mannopyranosyl and a-glucopyranosyl glycoprotein components of EPS (yellow). The EPS formed by the C. albicans was developed on npTi and glass surfaces after a 3-day incubation period. The blue arrow indicates the EPS surrounding attached cells on npTi and glass. The cell body was detected underneath the EPS, indicated by the red dashed circle. By contrast, attached cells on pTi were not enclosed by any EPS. Scale bars are 5 µm.