Figure 1. Mechanisms by which OCs couple bone resorption to bone formation.
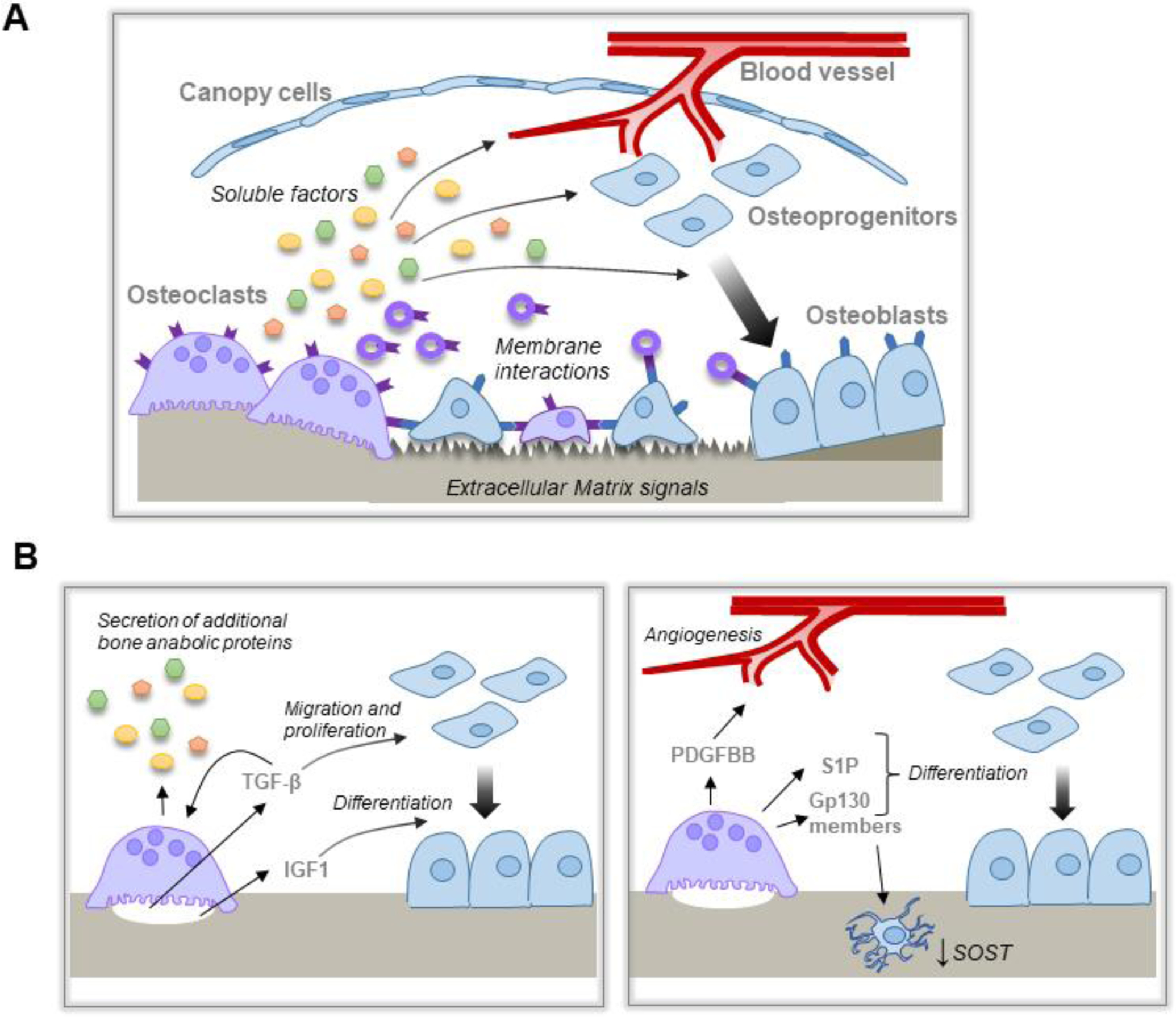
A, Schematic overview of the proposed mechanisms by which OC and resorption are coupled to bone formation. OC resorption releases matrix derived and OC-derived soluble factors and/or EVs that act on multiple cell lineages within the BRC to promote bone formation. OC membrane factors, including on EVs, interact with cognate receptors on cells within the BRC. In addition, altered bone matrix promotes optimal bone formation at sites of bone resorption. B, Matrix derived factors (left panel) released during bone resorption stimulate differential effects on osteoblast migration and proliferation vs differentiation. Matrix derived TGF-β also induces expression of other bone anabolic proteins. OC expression of additional factors (right panel) induce angiogenesis, osteoblast differentiation, and indirect effects on bone formation through the osteocytes.
