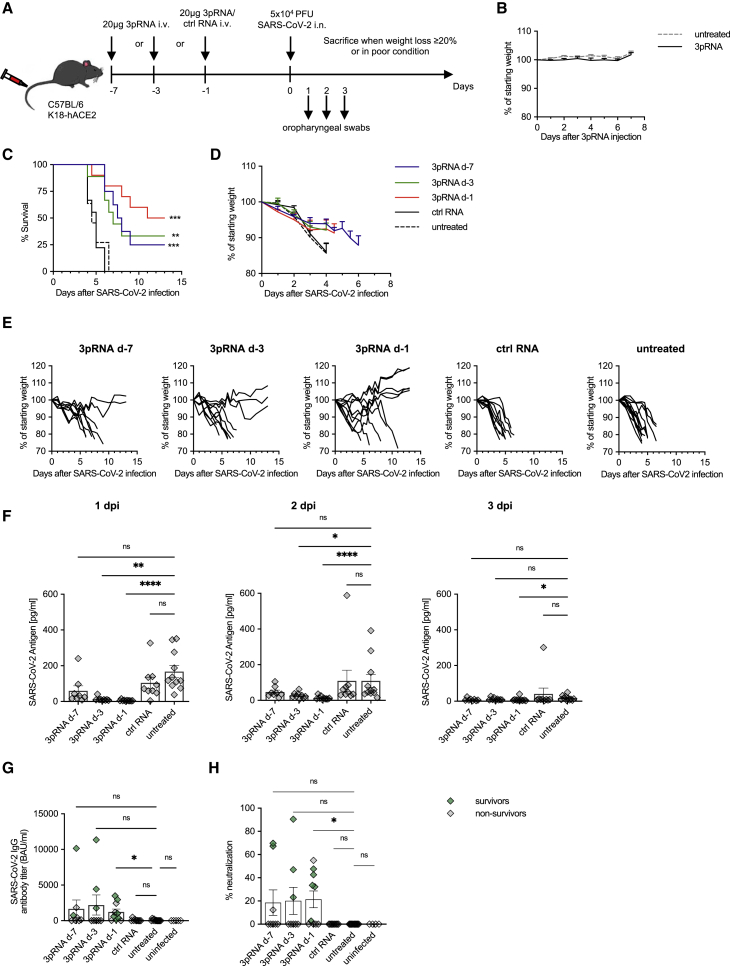
Figure 1.
Prophylactic RIG-I stimulation protects mice from lethal SARS-CoV-2 infection
(A) Experimental setup. K18-hACE2wt/tg mice were i.v. injected with 20 μg 3pRNA or control RNA complexed to in vivo jetPEI on the indicated days. On day 0 (d-0), mice were infected intranasally with 5 × 104 PFU SARS-CoV-2 virus. Oropharyngeal swabs were obtained on d-1 to d-3 post-infection (dpi). Disease development and survival were monitored up to twice daily until 13 dpi. (B) Weight development of 3pRNA-treated animals. Plotted are the means ± SEMs of 2 independent experiments (3pRNA n = 8, untreated n = 11). (C–E) Kaplan-Meier curve (C) and (D) weight loss (pooled) of SARS-CoV-2-infected animals. (E) Individual weight loss over time of each SARS-CoV-2 infected mouse until reaching the endpoint criteria or 13 dpi. (F) SARS-CoV-2 antigen ELISA of oropharyngeal swab material on 1 dpi to 3 dpi. (G) Quantification of anti-SARS-CoV-2-specific IgG antibody titers in sera of SARS-CoV-2-infected animals collected at their individual time of death or 13 dpi. (H) Percentage of inhibition of SARS-CoV-2 S1/RBD-hACE2 interaction by sera of SARS-CoV-2-infected animals collected at their individual time of death or 13 dpi. (C, D, F–H) Plotted are the means ± SEMs (3pRNA d-7 n = 8, 3pRNA d-3 n = 9, 3pRNA d-1 n = 10, ctrl RNA d-1 n = 9, untreated n = 11). The data are pooled from 2 independent experiments. The statistical significance was calculated by log rank Mantel-Cox test (B) and the non-parametric Kruskal-Wallis test with Dunn’s multiple testing (F and G). ∗p < 0.05, ∗∗p < 0.01, ∗∗∗p < 0.001, ∗∗∗∗p < 0.0001.