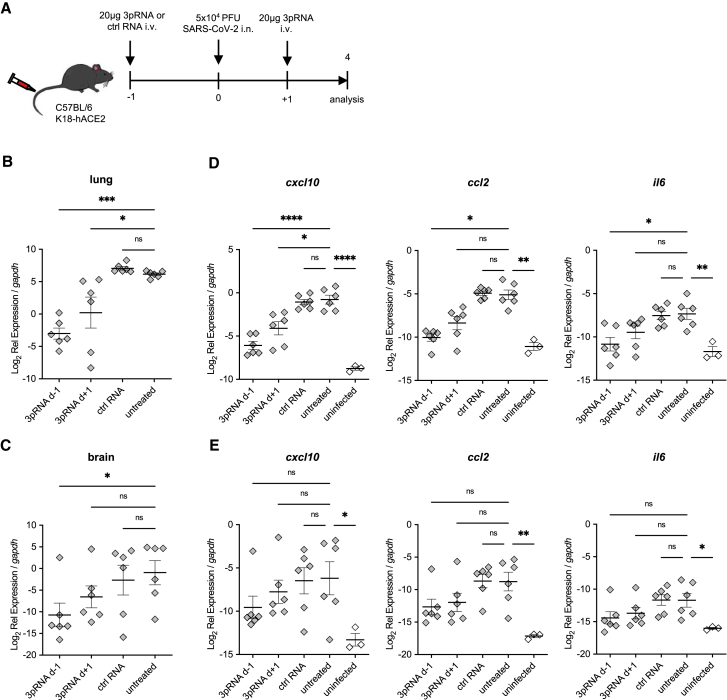
Figure 3.
Reduced viral burden and inflammation in SARS-CoV-2-infected lungs upon RIG-I ligand treatment
(A) Experimental setup. K18-hACE2wt/tg mice were i.v. injected with 20 μg 3pRNA or control RNA complexed to in vivo jetPEI 1 day before (3pRNA d-1) or after (3pRNA d+1) infection. Mice were infected intranasally with 5 × 104 PFU SARS-CoV-2 and sacrificed 4 dpi. (B and C) SARS-CoV-2 viral burden in the lungs (B) and in the brain (C) at 4 dpi. (D and E) Cytokine expression in the lungs (D) and brain (E) at 4 dpi. For (B)–(E), expression was quantified by qPCR relative to murine gapdh expression. Plotted are the means ± SEMs (n = 6, uninfected n = 3). The statistical significance was calculated by 1-way ANOVA (Welch) with Dunnett’s T3 multiple testing, when the data were lognormally distributed; otherwise, a non-parametric Kruskal-Wallis test with Dunn’s multiple testing was applied. ∗p < 0.05, ∗∗p < 0.01, ∗∗∗p < 0.001, ∗∗∗∗p < 0.0001.