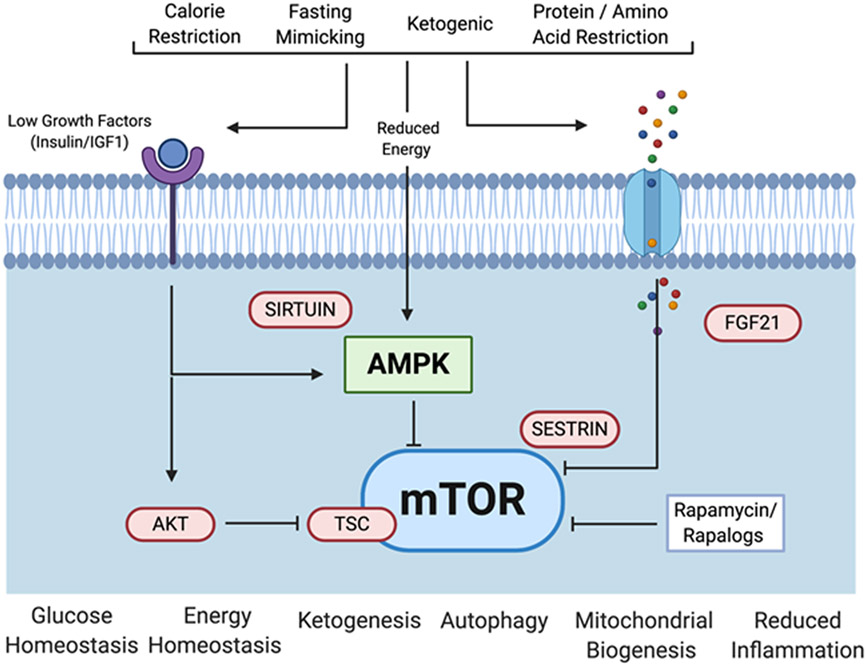
Figure 2.
Diet modalities, molecular mechanisms, and downstream consequences of anti-aging diets. Dietary interventions that impact aging in mice limit one or more of the major dietary macromolecules and elicit cellular responses via a complex nutrient sensing network. Key components of this network which have been implicated in effects on lifespan and healthspan in various laboratory model organisms include mechanistic Target Of Rapamycin (mTOR), Fibroblast Growth Factor 21 (FGF21), Adenosine Monophosphate-activated Protein Kinase (AMPK), insulin/Insulin Growth Factor 1 (IGF-1) receptors, AK strain Transforming (AKT), sestrin, and sirtuins. Figure created using Biorender.com.