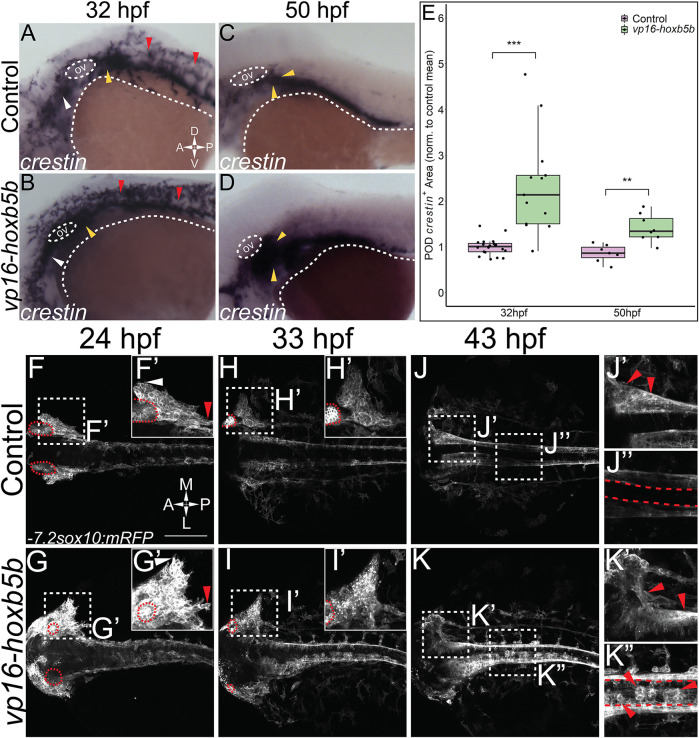
FIGURE 2.
Elevated Hoxb5b activity globally increases both number and localization of neural crest cells. (A–D) in situ hybridization for NCC using a crestin probe at both 32 hpf (A,B) and 50 hpf (C,D). crestin + domains for embryos injected with 15 pg of vp16-hoxb5b mRNA (B,D) were expanded in the post-otic (yellow arrowheads), cranial (white arrowheads), and spinal cord (red arrowheads), compared to uninjected embryos (A,C). (E) Quantification of expanded vagal crestin + domains shows significant expansion at both 32 hpf (control n = 27; vp16-hox5b n = 21; p = 3.03 × 10–5) and at 50 hpf (control n = 7; vp16-hox5b n = 8; p = 0.00114). (F–K) Maximum intensity projection stills taken from confocal time lapse movies of sox10:mRFP embryos. Controls (n = 2) were compared to 30 pg vp16-hoxb5b injected embryos (n = 4), examined from 24 hpf to 43 hpf and serially imaged along the dorsal aspect of the vagal domain. mRFP+ NCCs are grossly expanded in the vagal domain (G,G’ arrowheads) over controls (F,F’, arrowheads). This expansion persists through the course of development, resulting in ectopically localized cells along the dorsal aspect of the embryo (K”) and in the post-otic pool (K’). Scale Bars in (F): 100 μM. Anterior: Left.