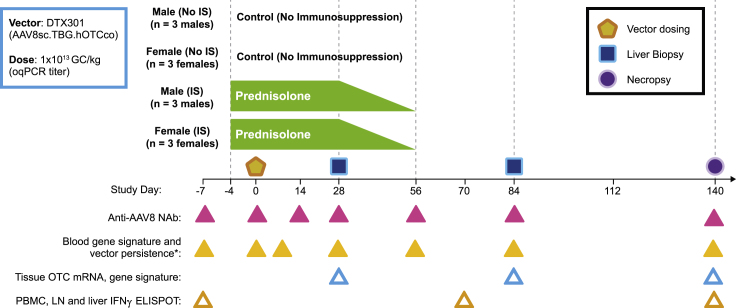
Figure 1.
Study design
Cynomolgus macaques were administered intravenously (i.v.) with 1 × 1013 genome copies (GCs)/kg of AAV8sc.TBG.hOTCco with no immunosuppression (IS) or prednisolone (1 mg/kg/day). Prednisolone was initiated 4 days prior (day −4) to vector administration and tapered between days 28 and 56 by approximately 25% per week. Two consecutive liver biopsies were performed on all animals on days 28 and 84, respectively. Necropsy and terminal collections were performed on day 140. Anti-AAV8 neutralizing antibodies (NAbs), vector DNA and IFN gene signature in the blood, vector DNA, human codon-optimized OTC (hOTCco) messenger RNA (mRNA), IFN gene signature in the liver, and IFN γ ELISpot were evaluated in individual macaques at the indicated time points (triangles). ∗For the IFN signature in the blood, day 0 samples were collected both pre dose and 6 h post dose. LN, lymph node; oqPCR, optimized quantitative polymerase chain reaction; PBMCs, peripheral blood mononuclear cells.