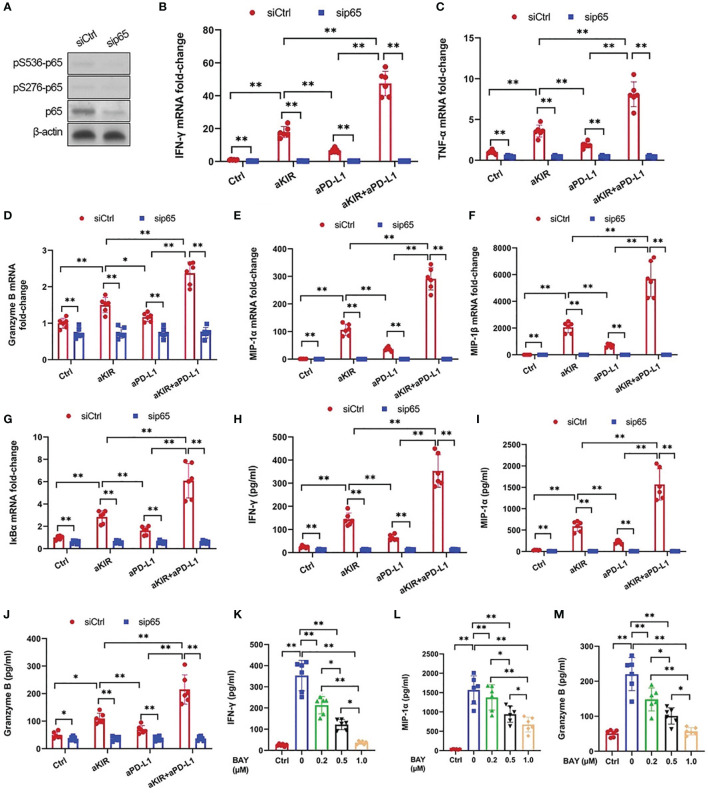
Figure 4.
Lirilumab and Avelumab Co-Engagement Upregulates Cytokine and Granzyme B Expression in a NF-κB-Dependent Manner. (A) NK cells were transfected with 300 pmol control siRNA (siCtrl) or anti-p65 siRNA (sip65) for 24 h. Cells were rested for another 24 h, and lysates were immunoblotted for p65 and β-actin. (B-G) IL-2-primed NK cells transfected with siCtrl or sip65 were mixed with autologous target cells and stimulated with aKIR and/or aPD-L1 for 3 h. Relative mRNA levels of (B) IFN-γ, (C) TNF-α, (D) granzyme B, (E) MIP-1α, (F) MIP-1β, and (G) IκBα were determined by real-time PCR and normalized to β-actin mRNA expression. (H-J) Transfected IL-2-primed NK cells were mixed with autologous target cells and stimulated as in (B-G) for (H, I) 8 h or (J) 2 h. (H) IFN-γ, (I) MIP-1α, and (J) Granzyme B were measured by ELISA. (K–M) IL-2-primed NK cells were pretreated with the NF-kB inhibitor BAY11-7082 (BAY) at the indicated doses for 1 h, mixed with autologous target cells, and stimulated with both aKIR and aPD-L1 for (K, L) 8 h or (M) 2 h. (K) IFN-γ, (L) MIP-1α, and (M) Granzyme B were measured by ELISA. *P < 0.05, **P < 0.01 [(B–J) two-way ANOVA (mAb factor × transfection factor), (K–M) one-way ANOVA]. n=3 biological replicates×3 technical replicates.