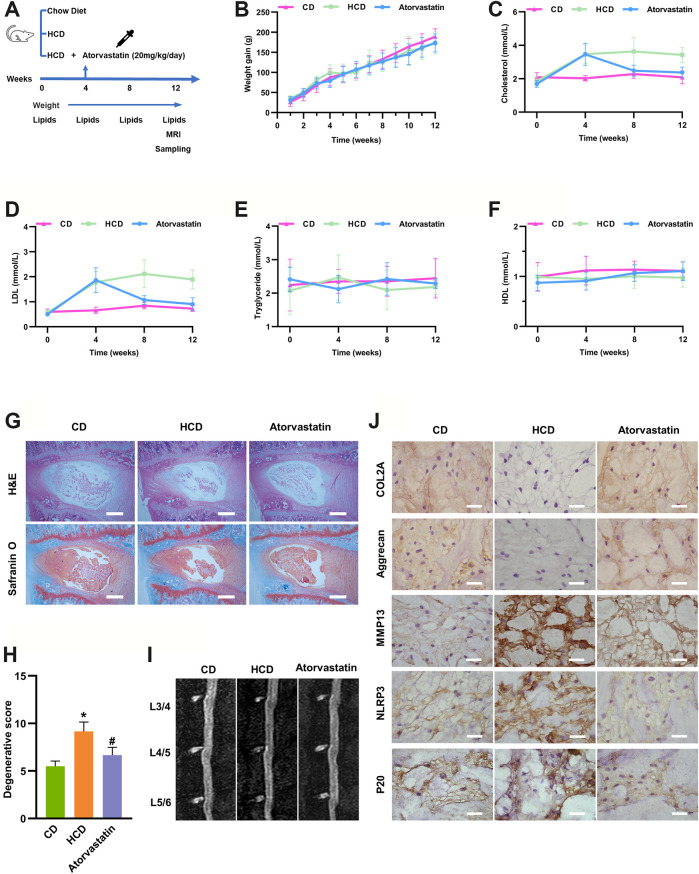
FIGURE 4.
Hypercholesterolemia induces IDD and pyroptosis-associated molecular changes, which were attenuated by atorvastatin. (A) Workflow diagram of animal experiments (B) Weight gain was not significantly different among SD rats fed different diets at any week (n = 12). (C, D) Total serum cholesterol and LDL concentrations of SD rats fed different diets at different weeks (n = 12). (E, F) Serum HDL (E) and triglyceride concentrations (F) of SD rats fed different diets at different weeks (n = 12). (G, H) H&E and Safranin O/Fast green staining of the lumbar intervertebral discs of SD rats showing that cholesterol induced IDD in the HCD group after 3 months of specific diets and that atorvastatin reversed this effect (bar = 500 μm). *p < 0.05 compared with CD group; # p < 0.05 compared with HCD group. (I) Representative sagittal lumbar MRI scans of SD rats fed different diets (J) The protein expression levels of the ECM components COL2A and aggrecan, catabolic metabolism marker MMP13, and pyroptosis-associated biomarkers NLRP3 and p20 were measured by IHC (bar = 20 μm). The data are presented as the mean ± SD. CD, chow diet.