FIGURE 3.
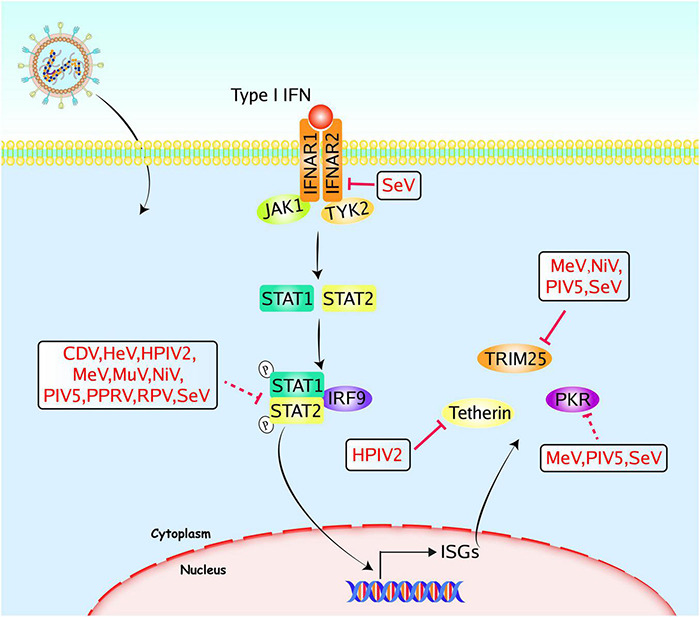
Paramyxoviruses accessory proteins-mediated evasion of the IFNAR-JAK-STAT signaling pathway. Following the binding of cytokines to the specific receptors, STATs are activated by members of the JAK family. Then they dimerize and translocate to the nucleus and regulate the expression of target genes, including ISGs. Accessory proteins from paramyxoviruses interact with adaptors to block the signal transduction, and some accessory proteins directly target ISGs to evade the innate immune responses. The V proteins of CDV, HeV, HPIV2, MeV, MuV, NiV, PIV5, PPRV, RPV, and SeV could inhibit STAT1/STAT2 mediated signaling pathways. The SeV C protein could inhibit IFNAR2, and the V proteins of MeV, NiV, PIV5, and SeV could inhibit TRIM25. The HPIV2 V protein could inhibit tetherin, the C proteins of MeV or SeV, and the MeV V protein could inhibit PKR. The PIV5 P and V proteins could inhibit the activation of PKR. Red solid lines indicate confirmed interactions between adaptors and accessory proteins, and red dashed lines indicate uncertain interactions or unknown underlying mechanisms; P, phosphate.
