Figure 1.
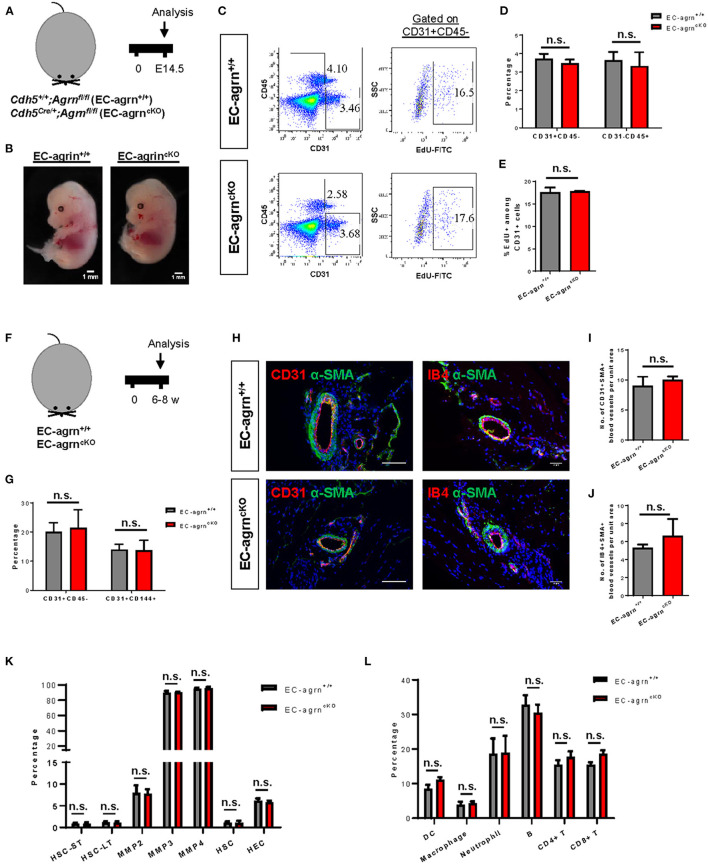
Endothelial agrin is dispensable for endothelial and haematopoietic cell development. (A) Schematic diagram showing the experimental design in embryos of Cdh5Cre/+;Agrnfl/fl (EC-agrncKO) and Cdh5+/+;Agrnfl/fl (control, EC-agrn+/+) mice. (B) Embryos harvested at embryonic day (E) 14.5 showing no gross difference after endothelial loss of agrin, scale bars: 1 mm. (C) Flow cytometric analyses showing the distribution of CD31+CD45− ECs, CD31−CD45+ haematopoietic cells, or CD31+CD45−EdU+ proliferating ECs purified from the embryos. (D,E) Quantification of (C) showing no significant difference in the percentage of (D) ECs and haematopoietic cells or (E) proliferating ECs after endothelial loss of agrin in embryos. (F) Schematic diagram showing experimental design in adult mice. (G) Quantification of flow cytometric analyses showing no significant difference in the percentage of ECs and haematopoietic cells after endothelial loss of agrin in adult mice. (H) Immunostaining on frozen sections for α-SMA (green), nuclear counterstain by DAPI (blue) and CD31 (red) or IB4 (red), scale bars: 100 um. (I,J) Quantification of (H) showing no significant difference in the absolute number of (I) CD31+αSMA+ or (J) IB4+αSMA+ blood vessels per unit area after endothelial loss of agrin in adult mice. (K,L) Quantification of flow cytometric data showing no significant difference in the percentage of (K) various haematopoietic stem or progenitor cells or (L) various white blood cell lineages after endothelial loss of agrin in adult mice. (D,E,G,I–L) Data are presented as mean ± S.E.M., n = 3–4, differences were determined by ANOVA and Turkey's HSD post-hoc test, n.s. denotes no significant difference.