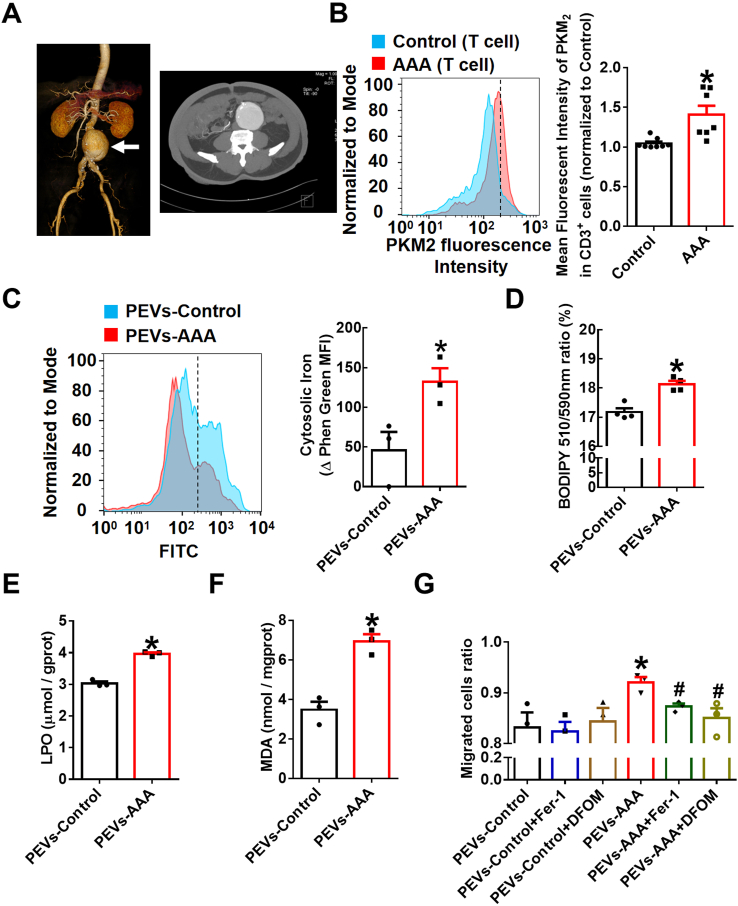
Fig. 7.
Extracellular vesicles from AAA patient plasma promote iron accumulation, lipid peroxidation and migration of macrophages.
(A) Representative computed tomography angiography (CTA) photographs of patients diagnosed with AAA. (B) Peripheral blood mononuclear cells (PBMCs) of AAA patients (n = 7) and control subjects (n = 8) were stained with fluorescently conjugated anti-CD3 and anti-PKM2 pAbs and then analyzed by flow cytometry. Quantification of PKM2 in T lymphocytes is shown in the right panel. Equal concentrations (20 μg/mL) of EVs isolated from AAA patient plasma (PEVs-AAA) or control plasma (PEVs-control) were cultured with THP-1 cells for 24 h n = 3–4. (C) Intracellular free iron levels were measured by a Phen Green SK probe. Quantification of the intracellular free iron level, which is inversely proportional to the Phen Green fluorescence intensity. Quantification of the oxidized BODIPY-C11 (emission: 590 nm)/reduced BODIPY-C11 (emission: 510 nm) ratio through flow cytometric analysis (D), lipid peroxidation (LPO) (E) and malondialdehyde (MDA) (F) in THP-1 cells. (G) Transwell migration assays of the PEV (20 μg/mL)-treated THP-1 cells in the upper chamber toward MCP-1 (20 ng/mL) in the lower chamber with or without the lipid peroxidation inhibitor Fer-1 (5 μmol/L) or the iron chelating agent DFOM (20 μmol/L). After 48 h of incubation, cells that had migrated to the bottom chamber or were still in the upper chamber were quantified by flow cytometry, and the migrated cell ratio was calculated (n = 3). The data are presented as the mean ± SEM. (B) *p < 0.05, compared with the control. (C–F) *p < 0.05, compared with PEVs-control. (G) *p < 0.05, compared with PEVs-control. #p < 0.05, compared with PEVs-AAA. The data were compared using Student's t-test (B–F) or one-way ANOVA followed by Tukey's multiple comparison test (G). (For interpretation of the references to colour in this figure legend, the reader is referred to the Web version of this article.)