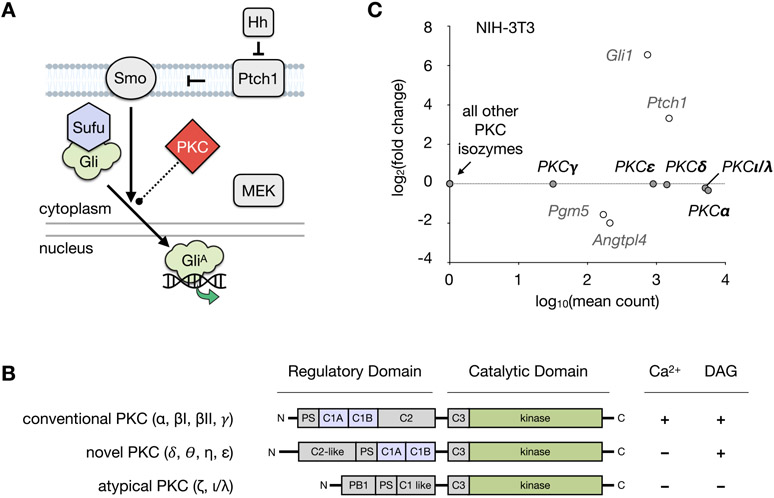
Figure 1.
Hedgehog signaling pathway and PKC. (A) Mechanism of Hedgehog pathway activation. Binding of Hh to Ptch1 releases suppression of Smo, whereupon activated Smo promotes dissociation of Gli proteins from Sufu. Gli proteins are converted into their active forms (GliA), which translocate to the nucleus and induce Hh pathway target gene expression. Activation of MEK/ERK signaling is independently able to regulate the formation of GliA. PKCs are reported to act directly on both proteins in the Hh pathway and MAP kinases. (Hh, Hedgehog; Ptch1, Patched 1; Smo, Smoothened; Gli, glioma-associated oncogene homologue; Sufu, Suppressor of Fused; MAP, mitogen-activated protein kinase, MEK, mitogen-activated protein kinase kinase; PKC, protein kinase C). (B) Regulation of PKC isozymes. Comparison of the conventional, novel, and atypical classes of the PKC family showing the regulatory domain cofactors required for enzyme activation. (C) RNA-seq analysis of PKC isozymes in NIH-3T3 cells after 30 h treatment with SAG (200 nM) or control (DMSO). PKC isozymes from each class are expressed in NIH-3T3 cells at significant levels, which are unaffected by SAG treatment. Mean count and fold change for the Hh pathway target genes Gli1, Ptch1, Pgm5, and Angtpl4 are shown for comparison. Differential expression was analyzed using DESeq2 with false discovery rate (FDR)-corrected p-value <0.01. Biological triplicates were analyzed for each condition.