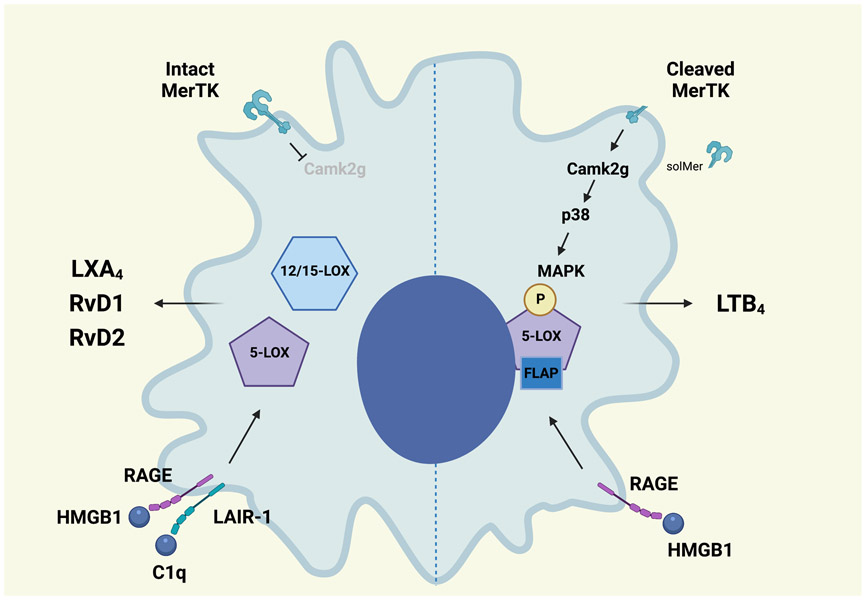
Figure 2. Nuclear localization of 5-lipoxygenase specifies lipid mediator production in response to receptor signaling.
Signaling by MerTK inhibits Calcium/calmodulin-dependent kinase 2γ (CaMK2g) activity and turns off a p38MAPK-MK2 cascade. This favors 5-LOX translocation to the cytoplasm where it is brought into proximity with 12/15-LOX and promotes lipoxin A4 (LXA4) production. Pro-inflammatory stimuli lead to MerTK cleavage and increased CaMK2g/p38MAPK-MK2 signaling that phosphorylates 5-LOX, enhancing its interaction with 5-LOX activating protein (FLAP). This promotes nuclear localization and leukotriene B4 (LTB4) production. The interaction of high-mobility group box 1 (HMGB1) with the receptor for advanced glycation end products (RAGE) also promotes phosphorylation of 5-LOX and increased LTB4 production. When complement 1q (C1q) is present, HMGB1 and C1q form a complex with RAGE and the leukocyte-associated Ig-like receptor-1 (LAIR-1). This tetramer favors cytoplasmic 5-LOX and increases SPM production. (Illustration credit: Ben Smith)