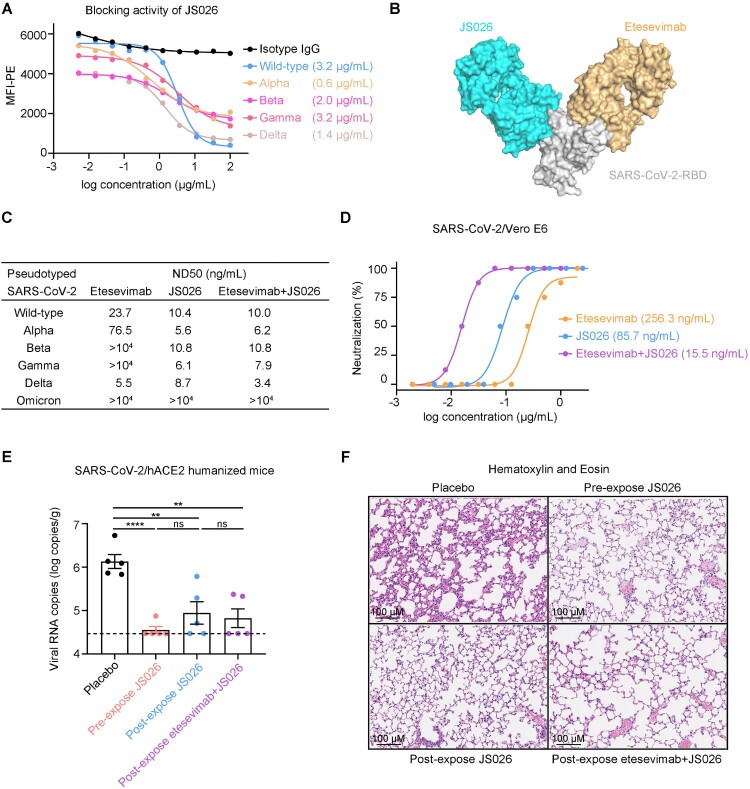
Figure 1.
Synergistic effects of JS026 and etesevimab in neutralizing SARS-CoV-2 VOCs. (a) mAb JS026 potently inhibited the binding of RBD from WT SARS-CoV-2 or VOCs to hACE2. HEK293T-hACE2 cells were stained with SARS-CoV-2-RBD proteins pre-incubated with isotype IgG or JS026 in flow cytometry-based assay. (b) Superimposition of JS026/RBD complex and etesevimab/RBD (PDB: 7C01) reveal the non-overlapping epitopes of etesevimab and JS026. The JS026-Fab, etesevimab-Fab, and SARS-CoV-2-RBD are coloured differently as indicated. (c,d) The neutralization activity of mAbs against SARS-CoV-2 VOCs. The mixtures of pseudotyped or authentic SARS-CoV-2 were incubated with serially diluted etesevimab, JS026, or the JS026/etesevimab cocktail. The mixtures were then added to HEK293T-hACE2 or Vero E6 cells for another incubation. One of three independent experiment data is shown. (e) Before SARS-CoV-2 challenge, the hACE2 transgenic mice (n = 8) in the prophylactic setting were intravenously infused with JS026. Then, 5 × 105 TCID50 SARS-CoV-2 was intranasally administered to animals and the therapeutic setting was injected with JS026, mAbs cocktail, or PBS as a vehicle control one day after challenging. SARS-CoV-2 titres in the lungs from five mice were measured by qRT-PCR (unpaired t-test, ns p > 0.05, ** p < 0.01, and **** p < 0.0001). (f) Histopathology examination of lung tissues (three mice) was performed at 5-day post-infection point. Scale bar: 100 μm.