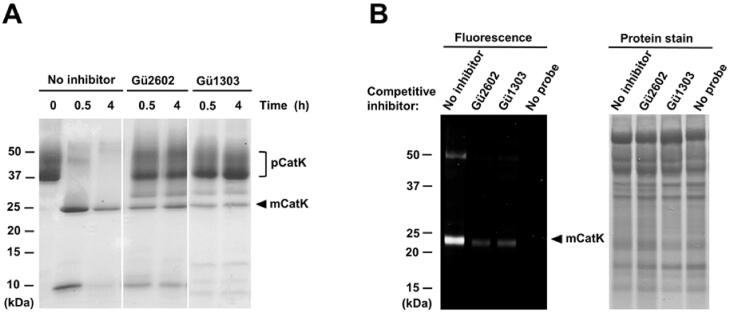
Figure 3.
The inhibitors Gü1303 and Gü2602 suppress the autocatalytic activation of the cathepsin K zymogen and target cathepsin K in cells. (A) The zymogen of cathepsin K (pCatK) was incubated in the presence and absence of inhibitor (10 µM) at pH 4.0, and the generation of mature cathepsin K (mCatK) was analysed at the indicated times. The reaction mixture was resolved by SDS-PAGE and visualised by protein staining. The positions of pCatK and mCatK are indicated; note mass heterogeneity of pCatK due to glycosylation61. (B) The U-2 OS cells were pre-treated with inhibitor (1 µM) for 3 h, followed by 24 h incubation with a fluorescent activity-based probe specific for cathepsin K40 (1 μM); quenching of the labelling reaction by competitive inhibition was analysed. Cell lysates were resolved by SDS-PAGE and visualised by fluorescence imaging (left) and protein staining (right). The position of mCatK is indicated. In control experiments, the probe or inhibitor was omitted.