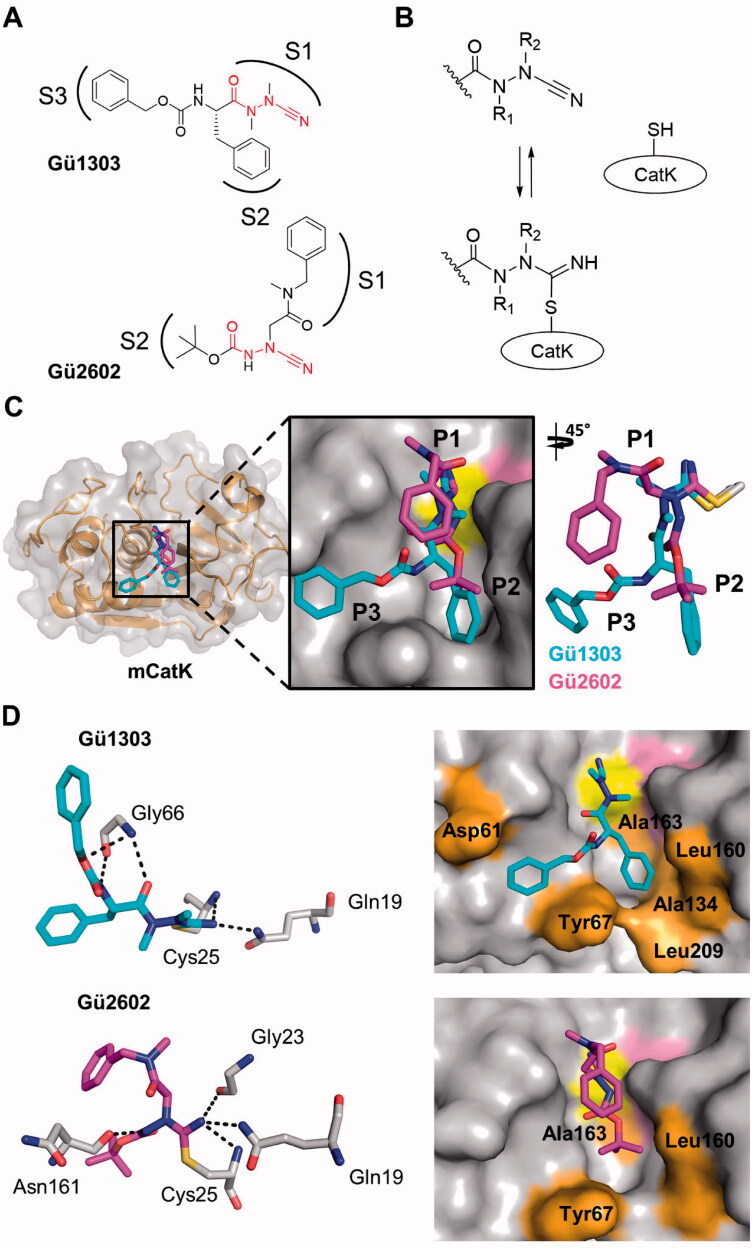
Figure 4.
Binding mode of the cyanohydrazide inhibitors Gü1303 and Gü2602 in the active site of mature cathepsin K. (A) Chemical structure of the azadipeptide nitrile inhibitor Gü1303 and 3-cyano-3-aza-β-amino acid inhibitor Gü2602; the binding subsites (S) are marked, and the cyanohydrazide warheads are in red. (B) Reactive warheads form a covalent reversible bond with the thiol of the catalytic cysteine residue of the enzyme; R1 and R2 are substituents on the N atoms of the warheads. (C) The zoomed-in view of the mCatK active site shows a superposition of the inhibitors bound to the S1 to S3 subsites (corresponding inhibitor positions P1 to P3 are indicated). mCatK is displayed in surface representation (grey); highlighted are the catalytic residues Cys25 (yellow) and His162 (pink). Inhibitors are shown in stick representation with carbon atoms in cyan for Gü1303 and magenta for Gü2602; heteroatoms have standard colour coding (O, red; N, blue; S, yellow). (D) Interaction of the inhibitors with active site residues of mCatK. Left panels: the hydrogen bond network formed between inhibitors and mCatK residues (dashed black lines). Inhibitors are coloured as in (C), and interacting enzyme residues are in grey; the side chain of the covalently linked catalytic cysteine residue Cys25 is depicted. Right panels: the surface representation of the mCatK active site shows enzyme residues (highlighted in orange) forming nonpolar interactions with the inhibitors (in stick representation); both inhibitors are in the same orientation.