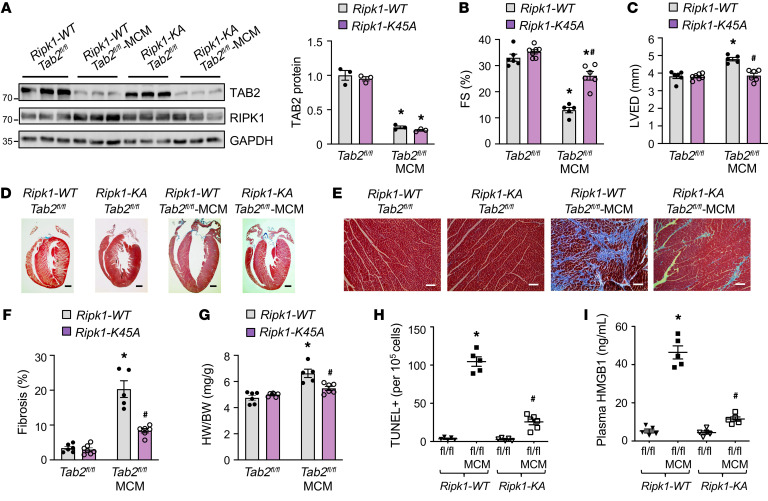
Figure 6. Genetic inactivation of RIPK1 rescues pathological cardiac remodeling and dysfunction in TAB2-deficient mice.
(A) Western blot and quantification of cardiac TAB2 expression from mice of the indicated genotypes 2 weeks after tamoxifen treatment. *P < 0.05 versus Tab2fl/fl. n = 3. (B and C) FS and LVED measured by echocardiography from mice of the indicated genotypes 2 weeks after tamoxifen treatment. *P < 0.01 versus Tab2fl/fl; #P < 0.05 versus Ripk1-WT Tab2fl/fl-MCM. n = 5–7. (D and E) Low- and high-magnification images of Masson’s trichrome–stained cardiac sections from mice indicated in A–C. Scale bars: 1 mm in D; 50 μm in E. (F) Myocardial fibrosis quantified by MetaMorph software. *P < 0.01 versus Tab2fl/fl; #P < 0.05 versus Ripk1-WT Tab2fl/fl-MCM. n = 5–7. (G) Heart weight to body weight ratio (HW/BW) in mice of the indicated genotypes. *P < 0.05 versus Tab2fl/fl; #P < 0.05 versus Ripk1-WT Tab2fl/fl-MCM. n = 5–7. (H) TUNEL-positive myocytes in cardiac sections from mice of the indicated genotypes. *P < 0.05 versus Tab2fl/fl; #P < 0.05 versus Ripk1-WT Tab2fl/fl-MCM. n = 5–7. (I) Plasma HMGB1 levels from mice of the indicated genotypes. *P < 0.01 versus Tab2fl/fl; #P < 0.05 versus Ripk1-WT Tab2fl/fl-MCM. n = 5–7. Statistical analysis was performed using 2-way ANOVA with Tukey’s multiple-comparison test.