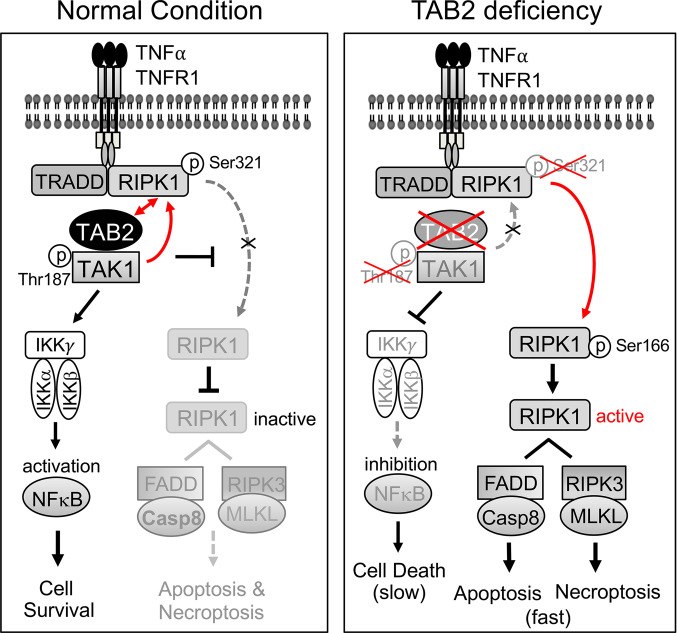
Figure 7. Proposed model: TAB2 acts as a key suppressor of RIPK1 kinase activation and RIPK1-dependent apoptotic and necroptotic signaling.
In cardiomyocytes, TAB2 plays an indispensable role in mediating TAK1-RIPK1 interaction, which leads to RIPK1 phosphorylation at Ser 321, preventing RIPK1 kinase activation and RIPK1-dependent apoptosis/necroptosis. TAB2 is also essential for TNFR1-mediated activation of the NF-κB prosurvival pathway. With TAB2 deficiency, TAK1-RIPK1 interaction is disrupted, leading to reduced phospho-RIPK1 at Ser 321, which promotes RIPK1 kinase activation and the induction of RIPK1-FADD-caspase-8 apoptotic complex and RIPK1-RIPK3 necroptotic complex. Moreover, ablation of TAB2 also blocks TAK1 activation, leading to NF-κB inhibition and a slow cell death response distinct from RIPK1-dependent apoptosis/necroptosis.