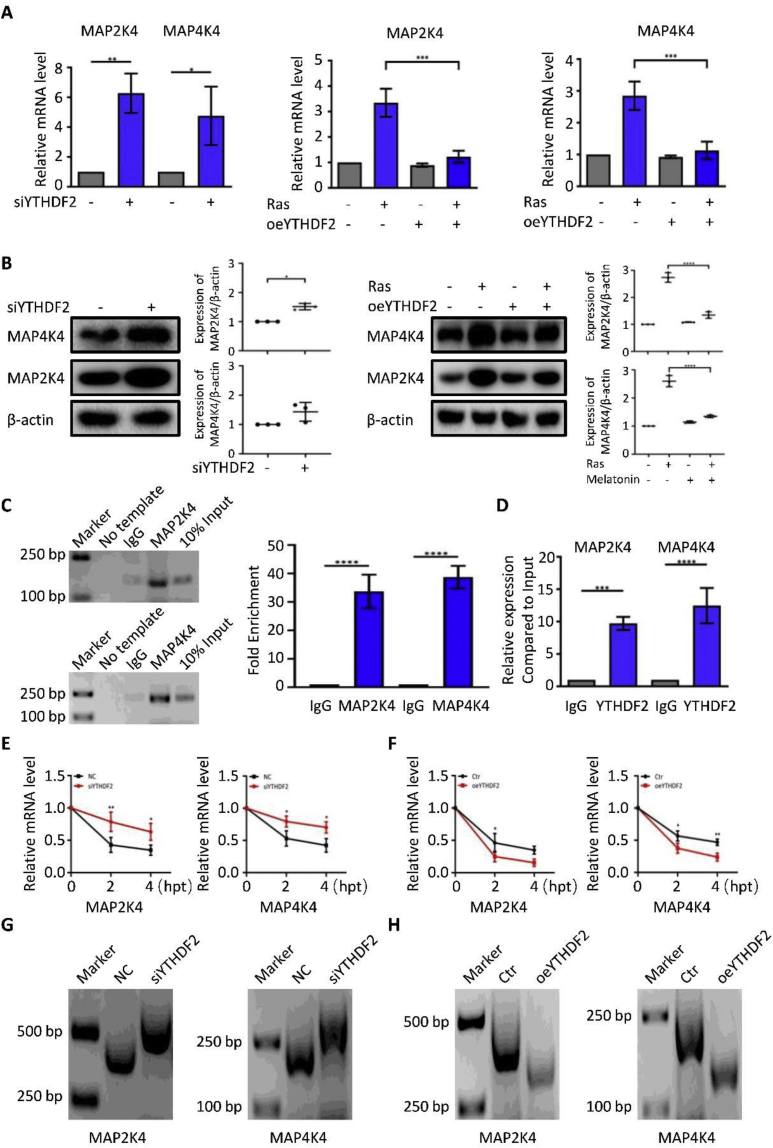
Figure 4.
Melatonin regulates the stability of MAP2K4 and MAP4K4 mRNAs in a YTHDF2-dependent manner. (A) The expression levels of MAP2K4 and MAP4K4 in HOSEpiCs that were transfected with negative control siRNA (NC), siYTHDF2 or empty vector (Ctr), and oeYTHDF2 and subjected to retrovirus-mediated expression of H-RasV12 for 8 days were measured using RT-PCR. (B) The protein levels of MAP2K4 and MAP4K4 levels were measured using Western blotting. (C) MeRIP-qPCR analysis of m6A abundance in MAP2K4 and MAP4K4 mRNAs. (D) MAP2K4 and MAP4K4 gene-specific YTHDF2 RIP-qPCR assays in HOSEpiCs. The value obtained for the IgG was set to 1. Error bars indicate the mean ± standard error of the mean, n = 3. (E,F) HOSEpiCs that were transfected with negative control siRNA (NC), siYTHDF2 or empty vector (Ctr), and oeYTHDF2 were subjected to retrovirus-mediated expression of H-RasV12 for 8 days; then, 5 μg/mL actinomycin D was added to inhibit global mRNA transcription for 0 h, 2 h, and 4 h. MAP2K4 and MAP4K4 expression levels were measured using qRT-PCR. β-actin was used as a normalization reference. (G,H) Results of the PAT assay showing poly(A) tail lengths of the indicated transcripts with different MAP2K4 and MAP4K4 3′-UTRs. The results are shown as the mean ± standard deviation of three independent experiments. P < 0.05 and P < 0.01 were considered statistically significant using two-sided Student's t-test. ∗, P < 0.05; ∗∗, P < 0.01.