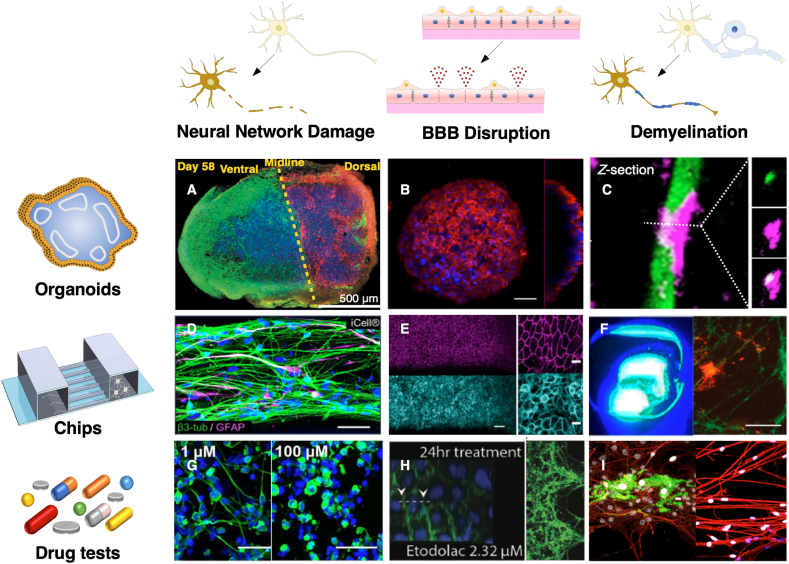
Fig. 3.
In vitro 3D brain models including brain organoids (upper lane, A-C) and brain-on-a-chips (middle lane, D-F). The row shows the observable side effects in the in vitro brain system, whereas the column shows brain-mimetic platforms and the representative cases of drug testing. For example, the side effects of drugs can be estimated through the observation of neurotoxicity, neuroinflammation, and neurodegeneration (bottom row, G-I), and the in vitro neural networks used to treat neurotoxic molecules are shown in the left column (A, D and G); (A) Fused cerebral organoids (Reproduced from Bagley et al. with permission [36]. Copyright 2017, Springer Nature.), (D) Neuron and astrocyte networks in microfluidics (Reproduced from Wevers et al. under the terms of the CC BY license [42]. Copyright 2016, Springer Nature.), (G) Neurotoxin molecule (methylmercury) treatment (Reproduced from Wevers et al. under the terms of the CC BY license [42]. Copyright 2016, Springer Nature.). For assessing neuroinflammation (middle column, B, E, and H), an in vitro BBB was fabricated and used to treat anti-inflammatory drugs; (B) BBB organoids (Reproduced from Bergmann et al. with permission [57]. Copyright 2018, Springer Nature.), (E) BBB chips (Reproduced from Park et al. under the terms of the CC BY license [58]. Copyright 2019, Springer Nature.), (H) Anti-inflammatory drug (Etodolac) treatment. (Reproduced from Shin et al. under the terms of the CC BY license [60]. Copyright 2019, Wiley). To estimate neurodegeneration (right column, C, F, and I), in vitro myelination models are fabricated and used to treat neurotoxin drugs; (C) oligodendrocyte and neuron organoids (Reproduced from Marton et al. with permission [67]. Copyright 2019, Springer Nature.), (F) Myelination in microfluidics (Reproduced from Lee et al. with permission [69]. Copyright 2016, American Chemical Society), (I) Neurotoxin drug (tetrodotoxin) treatment (Reproduced from Hyung et al. with permission [70]. Copyright 2019, Wiley).