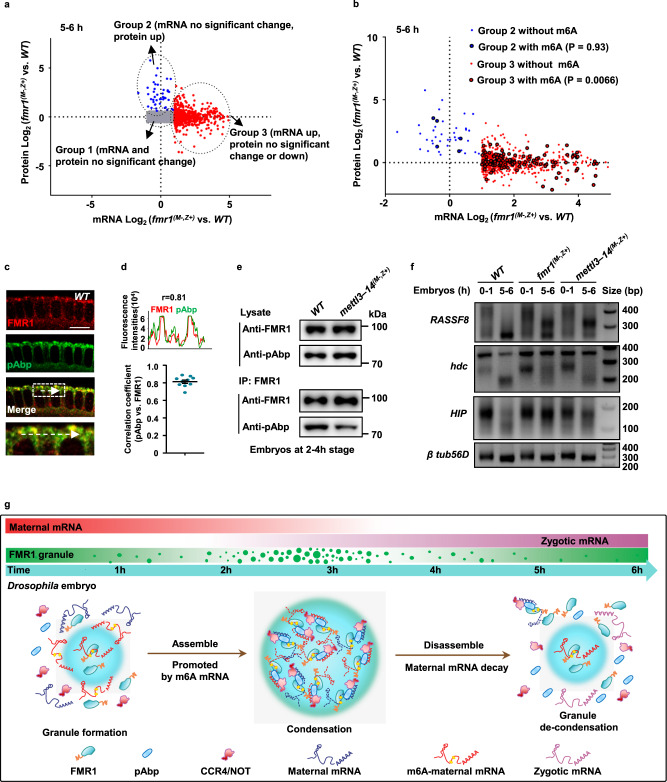
Fig. 5. FMR1 regulates the decay of its target maternal mRNAs in an m6A-dependent manner.
a Scatterplot integrating protein and mRNA levels were generated by using wild-type and fmr1 maternal mutant embryos at the 5–6-h stage. By comparing fold change of fmr1 maternal mutant versus wild-type embryos, three major groups were classified: Group 1 (gray), including the genes without any change in both protein and mRNA level; Group 2 (blue), including the genes with upregulated protein level, but limited mRNA level change; Group 3 (red), including the genes with upregulated mRNA level, but limited or decreased protein level change. b Group 2 and Group 3 were further analyzed to overlap with m6A marked genes. We identified that 537 out of 4814 genes (used for proteomic and transcriptomic analyses) were marked with m6A. In total, m6A modification (highlighted with black circle) was found in as few as 5 genes in Group 2 (two-sided chi-square test, P = 0.93), but in a significant portion of genes (116) in Group 3 (two-sided chi-square test, P = 0.0066). c Wild-type embryos (at the 2–3-h stage) were stained with anti-FMR1 (red) and anti-pAbp (green) antibodies. Representative figures of three independent experiments are shown. Scale bars, 10 μm. d Pearson’s correlation coefficients of line profiles of FMR1 and the indicated proteins (n = 10). Error bars indicate mean ± SEM. e Coimmunoprecipitation of FMR1 with pAbp in wide-type and mettl3–mettl14 double maternal mutants at 2–4-h embryonic stage. The lysates were immunoprecipitated with anti-FMR1 antibody, and western blot assays were performed to detect pAbp protein in each immunoprecipitation. Representative figures of two independent replicates are shown. f PAT assay results showing changes in poly(A)-tail length for the indicated transcripts in the 0–1 and 5–6-h embryos with indicated genotypes. Representative figures of three independent replicates are shown. g Model for dynamic condensation/de-condensation of FMR1 granules to regulate maternal mRNA decay in fly early embryos. Source data are provided as a Source Data file and Supplementary Data 4.