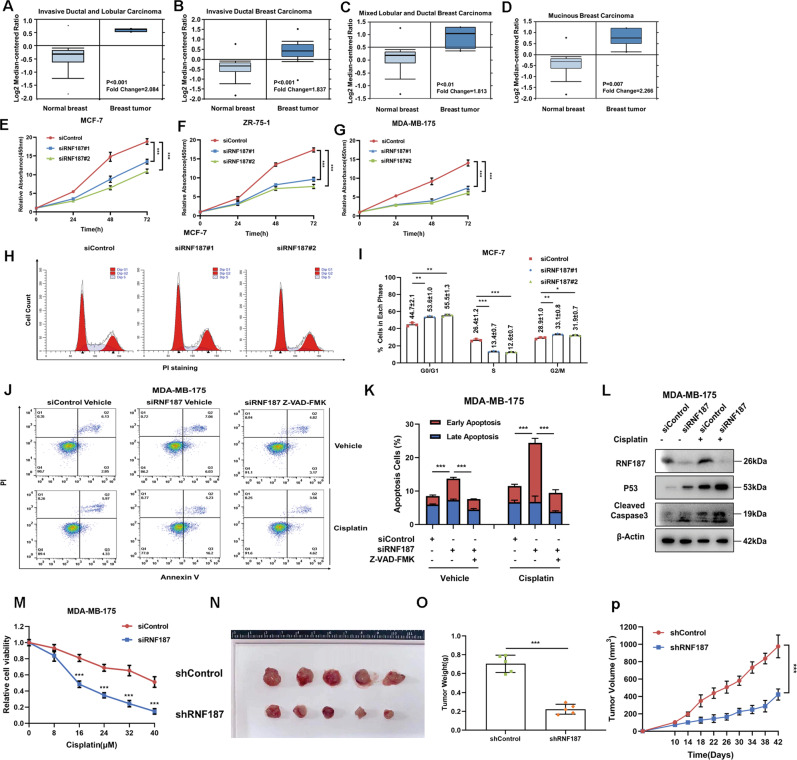
Fig. 1. RNF187 is elevated in breast tumors and is required for cancer cell growth and apoptosis resistance in luminal-type breast cancer.
A–D RNF187 mRNA levels are elevated in breast cancer samples compared with normal breast tissues in the ONCOMINE database (http://oncomine.org). E RNF187 depletion inhibits the proliferation of breast cancer cells. MCF-7 cells were transfected with 50 nM RNF187 siRNA or 50 nM control siRNA. Two independent siRNAs were used. After 24 h, a CCK-8 assay was used to determine the cellular metabolic activity at the indicated time points after transfection. Experiments were performed in triplicate. *P < 0.05; **P < 0.01; ***P < 0.001 for cell growth comparisons. F RNF187 depletion inhibits the proliferation of breast cancer cells. MDA-MB-175 cells were transfected with 50 nM RNF187 siRNA or 50 nM control siRNA. Two independent siRNAs were used. After 24 h, a CCK-8 assay was used to determine the cellular metabolic activity at the indicated time points after transfection. Experiments were performed in triplicate. *P < 0.05; **P < 0.01; ***P < 0.001 for cell growth comparisons. G RNF187 depletion inhibits the proliferation of breast cancer cells. ZR751 cells were transfected with 50 nM RNF187 siRNA or 50 nM control siRNA. Two independent siRNAs were used. After 24 h, a CCK-8 assay was used to determine the cellular metabolic activity at the indicated time points after transfection. Experiments were performed in triplicate. *P < 0.05; **P < 0.01; ***P < 0.001 for cell growth comparisons. H, I Cell cycle analysis to assess the effect of RNF187 knockdown in MCF-7 cells. MCF-7 cells were transfected with 50 nM RNF187 siRNA or 50 nM control siRNA. Two independent siRNAs were used. After 24 h, the cells were harvested, fixed with 70% ethanol, and stained with propidium iodide. The cells were subjected to FACS analysis. Experiments were performed in triplicate. *P < 0.05; **P < 0.01; ***P < 0.001 for cell proportion comparisons. Representative histograms and cell cycle phase distributions are shown in Fig. 1I, J, respectively. J, K RNF187 depletion promoted apoptosis in MDA-MB-175 cells, which effect could be rescued by the caspase-3 inhibitor (Z-VAD-FMK). MDA-MB-175 cells were transfected with siControl or siRNF187. After that, cells were treated with vehicle or 10 uM cisplatin in combination with 20 uM Z-VAD-FMK. After 24 h, cells were stained with PI and Annexin V. Then cells were subject to FACS analysis for the proportion of apoptotic cells. Each group was done in triplicates. *P < 0.05; **P < 0.01; ***P < 0.001 for comparison. L RNF187 depletion increased the cleaved caspase-3 protein level under both vehicle and cisplatin treatment conditions. MDA-MB-175 cells were transfected with siControl or siRNF187. Cisplatin (10 μM) was added to treat the cells for 6 h. Then, the cells were harvested for western blot analysis. RNF187, P53, and cleaved caspase-3 protein levels were determined by western blot analysis. Actin was used as the internal control. M RNF187 depletion sensitizes MDA-MB-175 cells to cisplatin-mediated inhibition. MDA-MB-175 cells were transfected with 50 nM siRNF187 or siControl. After 24 h, the cells were treated with cisplatin at the indicated concentration for 24 h. Cell viability was determined via a CCK-8 assay. N–P RNF187 depletion inhibits breast tumor growth in vivo. MCF-7 cells were stably transduced with lentiviral vectors carrying scrambled shRNA or RNF187 shRNA. Female NOD scid gamma (NSG) mice were implanted with slow-release 17β-estradiol pellets (0.72 mg/90-d release; Innovative Research of America) 1 day before MCF-7 tumor cell injection into the mammary fat pad (2 × 106 MCF-7 cells suspended in 100 µl of Matrigel solution). MCF-7 tumor xenografts were measured every 3–4 days, and tumor volumes were calculated as length × width2/2. Mice were sacrificed 6 weeks after tumor cell injection. Tumor growth curves, weights, and photographs are shown in panels N–P, respectively.