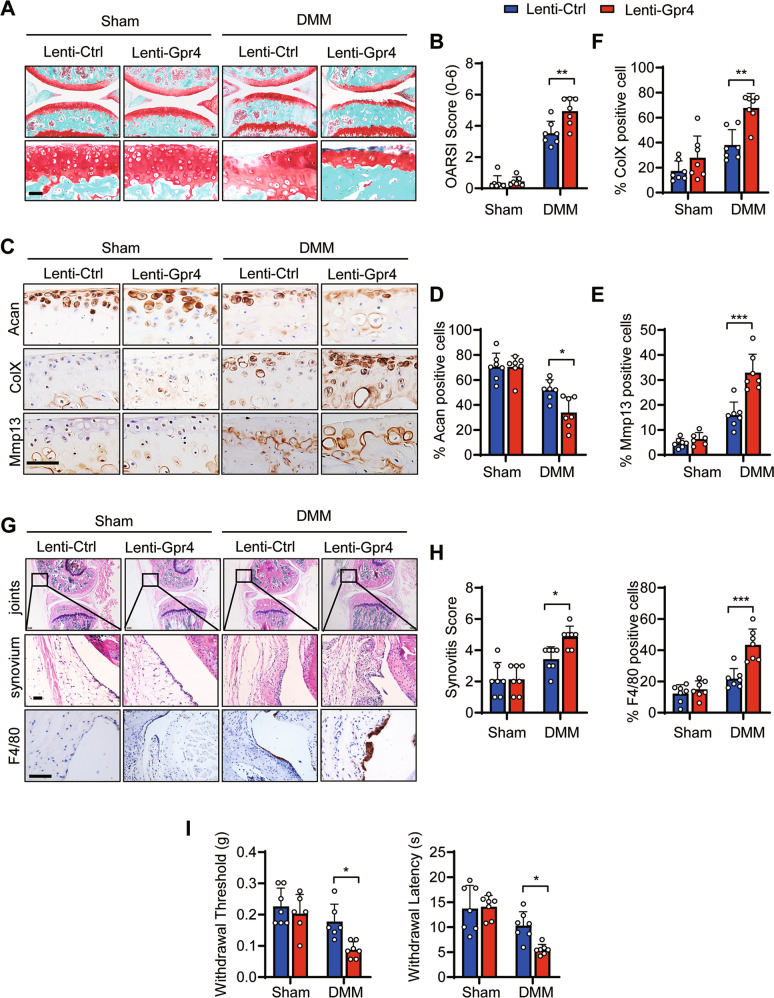
Fig. 2. Lentivirus-mediated overexpression of GPR4 in mouse joint accelerated the development of posttraumatic OA.
A, B Representative images of Safranin-O staining of mouse joints injected with lentivirus expressing GPR4 (Lenti-Gpr4) or empty control (Lenti-Ctrl). Four days after DMM surgery, the mice were IA injected with lentivirus once a week. Eight weeks later, the joints were collected and subject to Safranin-O staining (A). Scale bars, 50 μm. OARSI scores (B) were analyzed. Sham groups (n = 7 mice), DMM groups (n = 7 mice). Data are expressed as mean ± s.d. **p < 0.01 using two-way ANOVA followed by Tukey’s post hoc test. C–F Representative images of indicated antibody IHC staining of knee joint sections taken 8 weeks after DMM or Sham operation with Lenti-Gpr4 or Lenti-Ctrl injection. The corresponding quantitative analyses were shown in (D–F). Scale bars, 50 μm. n = 7 per group. Data are expressed as mean ± s.d. *p < 0.05, **p < 0.01, ***p < 0.001 using two-way ANOVA followed by Tukey’s post hoc test. G, H The joints were collected and subjected to H&E and IHC staining. Scale bars, 50 μm. G Synovitis scores were determined based on H&E staining (H left, n = 7) and F4/80 positive cells were quantified (H right, n = 7). Data are expressed as mean ± s.d. *p < 0.05, ***p < 0.001 using two-way ANOVA followed by Tukey’s post hoc test. I Von Frey assay (left) and thermal hyperalgesia test (right) were performed 8 weeks after DMM or Sham operation with Lenti-Gpr4 or Lenti-Ctrl injection. n ≥ 6. Data are expressed as mean ± s.d. *p < 0.05 using two-way ANOVA followed by Tukey’s post hoc test.