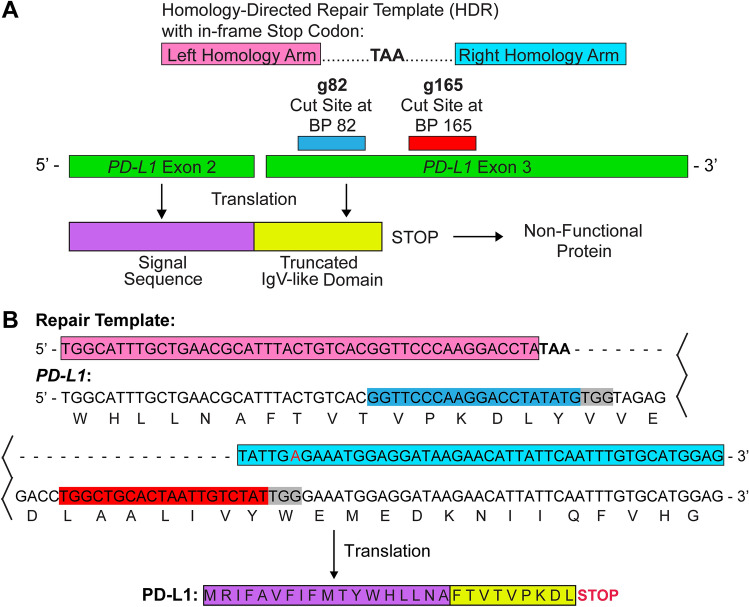
Figure 1.
Schematic of dual-sgRNAs and a HDR template for the CRISPR/Cas9 system. (A) sgRNA 82 (g82; cyan) and sgRNA 165 (g165; red) were chosen for PD-L1 gene-editing due to their high on-target and low off-target properties. g82 recognizes the forward strand of PD-L1 exon 3 (green) and cuts at approximately base pair (bp) 82. g165 recognizes the forward strand of exon 3 and cuts at bp 165. To promote PD-L1 gene-editing, a homology directed repair template (HDR) was designed to incorporate an in-frame stop codon (TAA). The left (pink) and right (light blue) homology arms recognize 45 bps of sequence on either side of the g82 and g165 cut sites, respectively. After gene-editing, only the signal sequence (purple) and a truncated IgV-like domain (yellow) of PD-L1 are translated. This leads to the production of a non-functional PD-L1 protein. (B) DNA sequence of PD-L1, the repair template, sgRNA’s, and the translated protein sequence after gene editing. Colored sequences in B match sequences labeled in (A). Additionally, the red (A) in the right homology arm indicates a single bp modification in the PAM sequence (grey) to prevent cutting of the repair template by the Cas9 enzyme.