FIGURE 2.
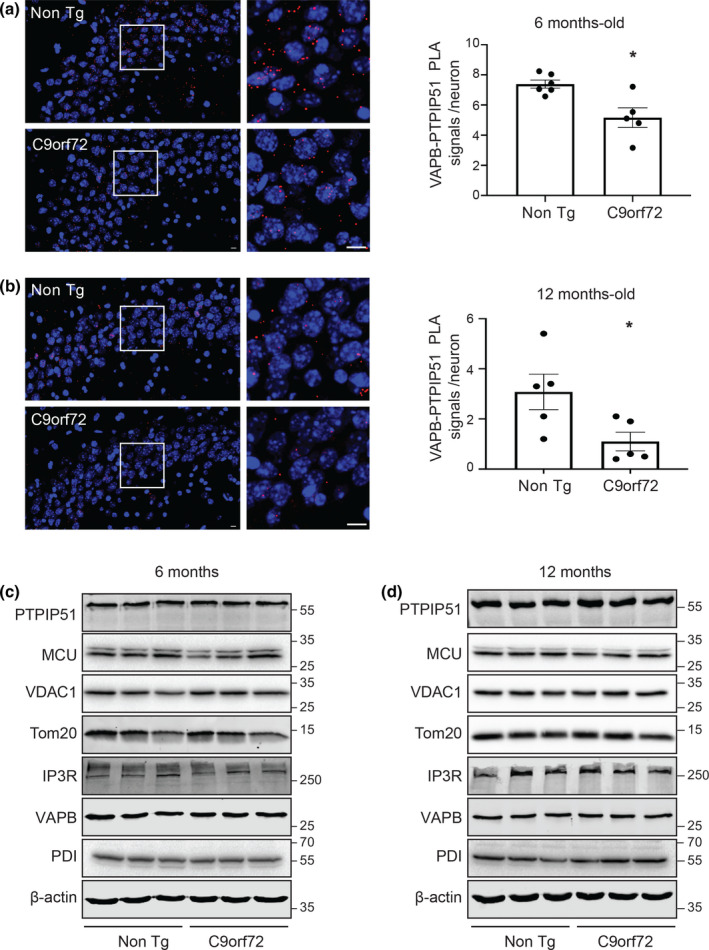
VAPB‐PTPIP51 interaction is disrupted prior to disease onset in affected hippocampal neurons in mutant C9orf72 transgenic mice but this does not involve changes in expression of brain VAPB, PTPIP51 or other key ER‐mitochondria Ca2+ exchange proteins. (a, b) Representative projected Z‐stack confocal images of VAPB‐PTPIP51 PLAs (Red) in C9orf72 transgenic and non‐transgenic littermate (Non Tg) CA3 hippocampal neurons at 6 and 12 months age as indicated. Samples were also stained with DAPI to show nuclei. Scale bars = 10 μm. Bar charts show numbers of PLA signals per neuron. N = 808 cells from 5 C9orf72 transgenic mice and N = 735 cells from 6 non‐transgenic mice in (a) and N = 1676 cells from 5 C9orf72 transgenic mice and N = 1370 cells from 5 non‐transgenic mice in (b). Data were analysed by Mann–Whitney U test. Error bars are SEM; *p ≤ 0.05. (c, d) C9orf72 transgenic mice do not display changes in expression of brain VAPB, PTPIP51 or other key ER‐mitochondria Ca2+ exchange proteins at either 6 (c) or 12 (d) months of age. Immunoblots for VAPB, PTPIP51, VDAC1, IP3R type 1, MCU, PDI, TOM20 and actin as a loading control are shown. Molecular mass markers are indicated in kDa. Quantifications (not shown) were made from 3 control and 3 C9orf72 transgenic mice at each age point as indicated. Signals were normalised to actin signals and data were analysed by Mann–Whitney U test; no significant differences between control and C9orf72 lines were detected for any protein
