FIGURE 6.
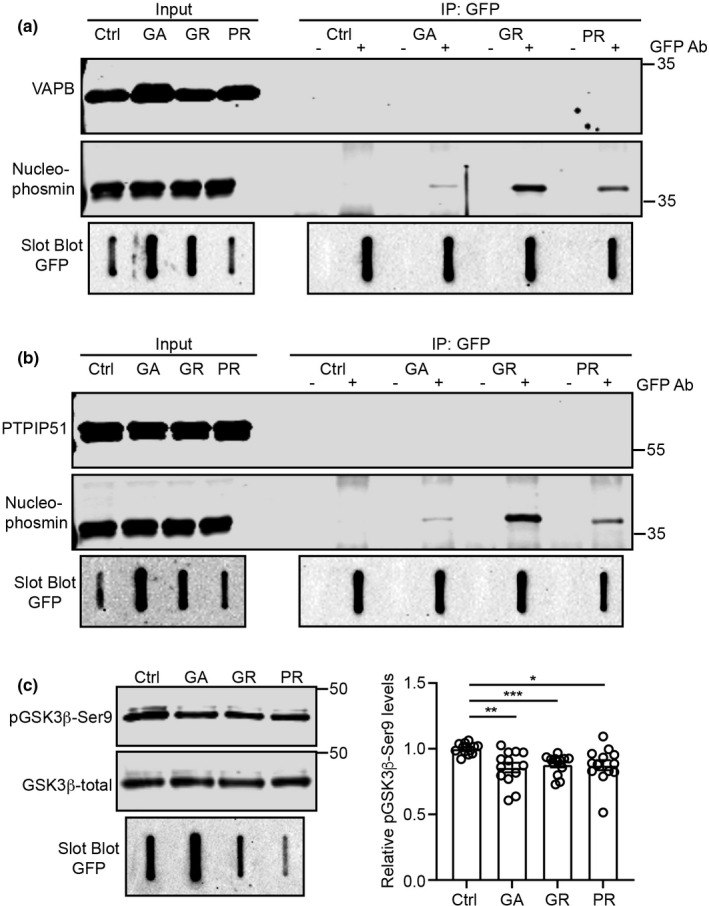
C9orf72 DPRs do not bind to either VAPB or PTPIP51 but activate GSK3β. (a, b) C9orf72 DPRs do not bind to either VAPB (a) or PTPIP51 (b). SH‐SY5Y cells were transfected with EGFP control plasmid (Ctrl) or EGFP‐tagged poly‐GA, poly‐GR or poly‐PR DPRs +myc‐VAPB or PTPIP51‐HA as indicated. DPRs were immunoprecipitated using rabbit anti‐GFP antibody and detected using mouse anti‐GFP antibody. VAPB and PTPIP51 were detected using mouse anti‐myc or anti‐HA antibodies to the epitope tags. Positive control endogenous nucleophosmin was detected using mouse anti‐nucleophosmin. DPRs were detected on slot blots; VAPB, PTPIP51 and nucleophosmin were detected after SDS‐PAGE on immunoblots. Both lysate inputs and immunoprecipitates (IP) are shown. (−) and (+) refer to absence or presence of the GFP antibody in the immunoprecipitates; N = 3. (c) C9orf72 DPRs activate GSK3β. SH‐SY5Y cells were transfected with EGFP control plasmid (Ctrl) or EGFP‐tagged poly‐GA, poly‐GR or poly‐PR DPRs and samples probed for total and serine‐9 phosphorylated GSK3β as indicated. Bar chart shows relative levels of serine‐9 phosphorylated inactive GSK3β following normalisation to total GSK3β signals. Data were analysed by Welch ANOVA and Games‐Howell's post hoc test, N = 13. Error bars are SEM, *p ≤ 0.05, **p ≤ 0.01, ***p ≤ 0.001
