Figure 4: Differential expression of gut homing integrins on hepatic and peripheral CD4+ T-cells in chronic liver disease.
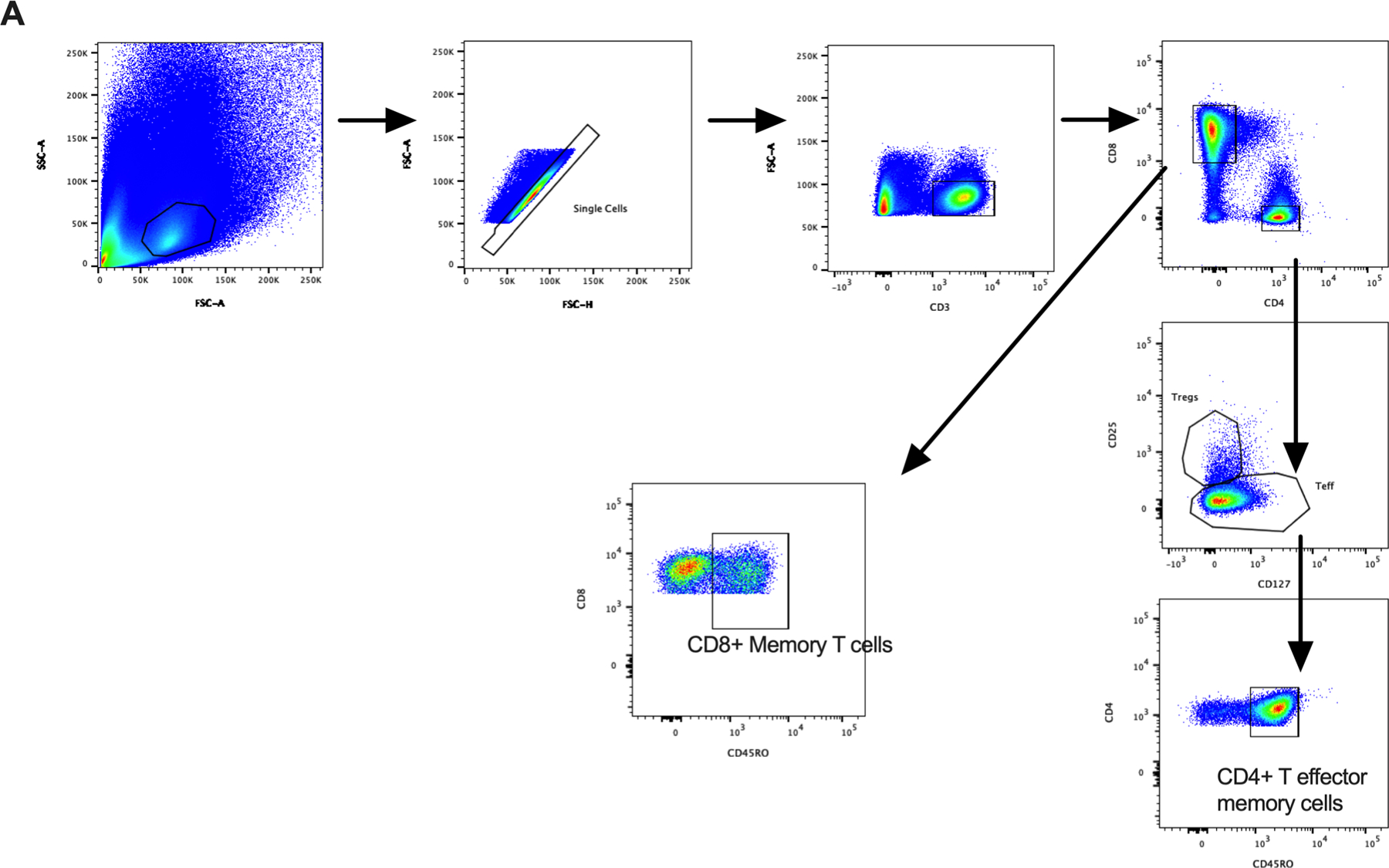
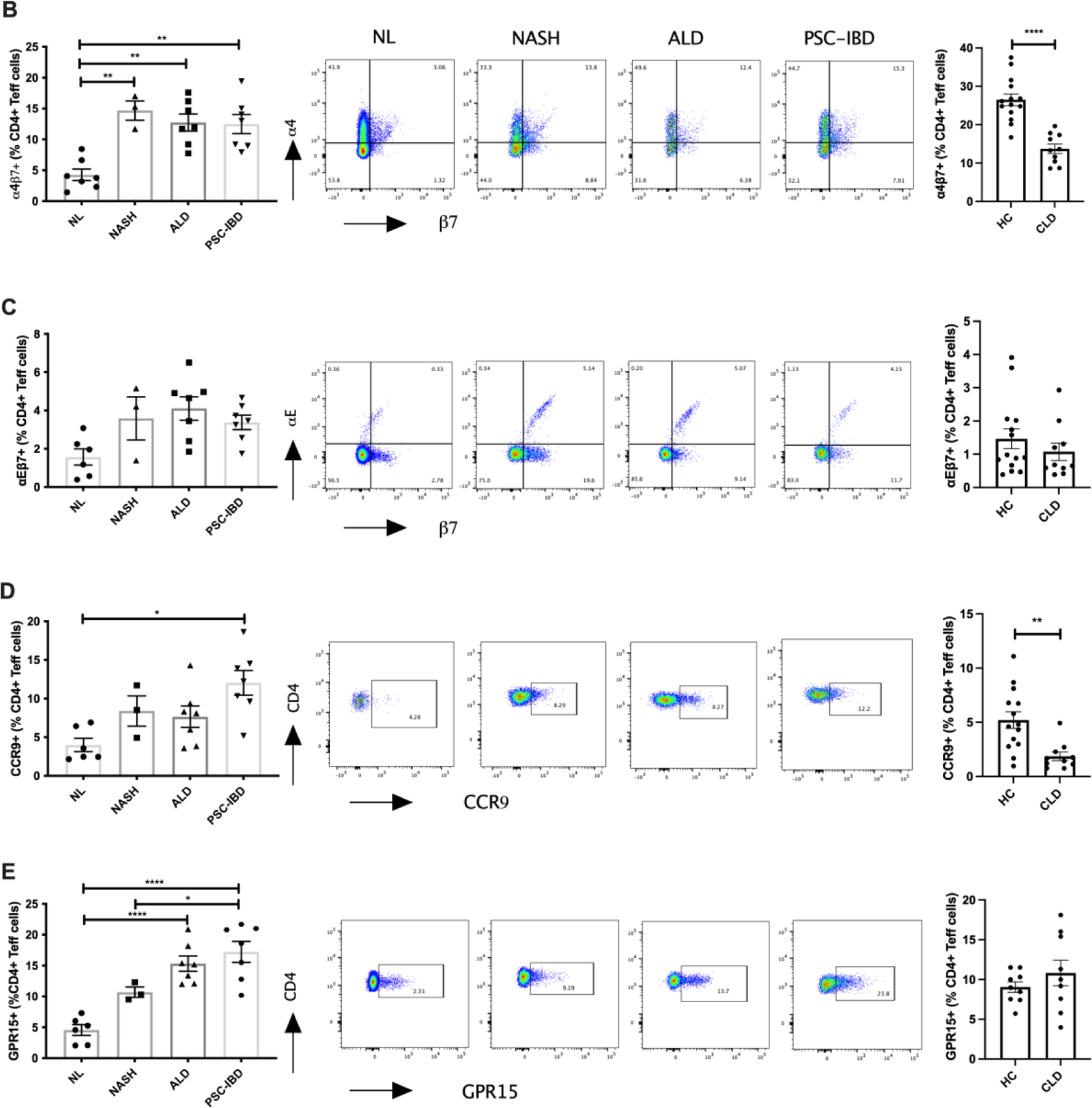
(A) Flow cytometry gating strategy for CD4+ T effector memory and CD8+ memory T-cells. Left panels: expression of gut homing integrins: (B) α4β7, (C) αEβ7, (D) CCR9 and (E) GPR15 on hepatic CD4+ T-cells (numbers expressed as a percentage of CD4+ T effector memory cells). Centre panels: Representative flow cytometry plots of gut homing integrins on hepatic CD4+ T-cells in normal liver (NL), non-alcoholic steatohepatitis (NASH), alcoholic liver disease (ALD) and primary sclerosing cholangitis with inflammatory bowel disease (PSC-IBD) (B-E). Right Panels (B-E): Differential expression of gut homing integrins on peripheral CD4+ T effector memory cells in NL and patients with chronic liver disease (CLD). Integrin positive cells were gated on and expressed as a percentage of CD3+CD4+CD127+CD45RO+ cells (T effector memory cells). *P ≤ 0.05; **P ≤ 0.01; ***P ≤ 001
