Figure 1.
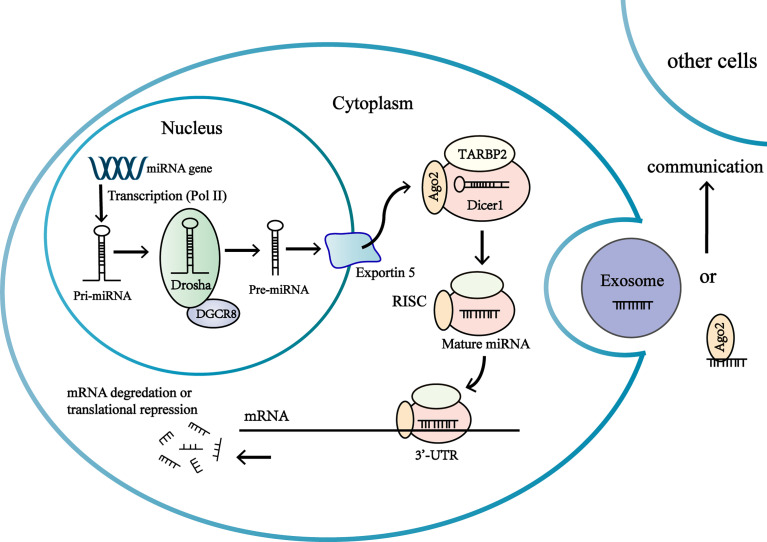
Biogenesis and function of miRNAs in the adrenocortical tumor cells. MiRNA genes are transcribed as primary miRNA (pri-miRNA) in nucleus. Pri-miRNA is processed by multiprotein complex to produce a precursor miRNA (pre-miRNA). The multiprotein complex consists of a double-stranded RNA (dsRNA)-binding protein DGCR8, a nuclear RNase III enzyme Drosha. The pre-miRNAs are transported from nucleus to the cytoplasm by exportin-5 (Exp-5). In the cytoplasm, the pre-miRNA are processed by the RNase III endonuclease Dicer protein and the double-stranded transactivation-responsive RNA-binding protein (TRBP), producing a short double-stranded (ds) miRNA duplex. One strand of miRNA duplex is next loaded into an Ago protein to form RISC, while the other one is degraded by cellular nuclease. RISC complex consists of Dicer, Argonaute 2 (Ago2), and the dsRNA-binding protein TRBP. The association of the miRNA-RISC complex binding to 3’-untranslated region (3’-UTR) of target mRNA leads to inhibition of protein translation or degradation of the mRNA. Extracellular miRNAs in extracellular vesicles or associated with RNA-binding proteins are involved in intercellular communications.