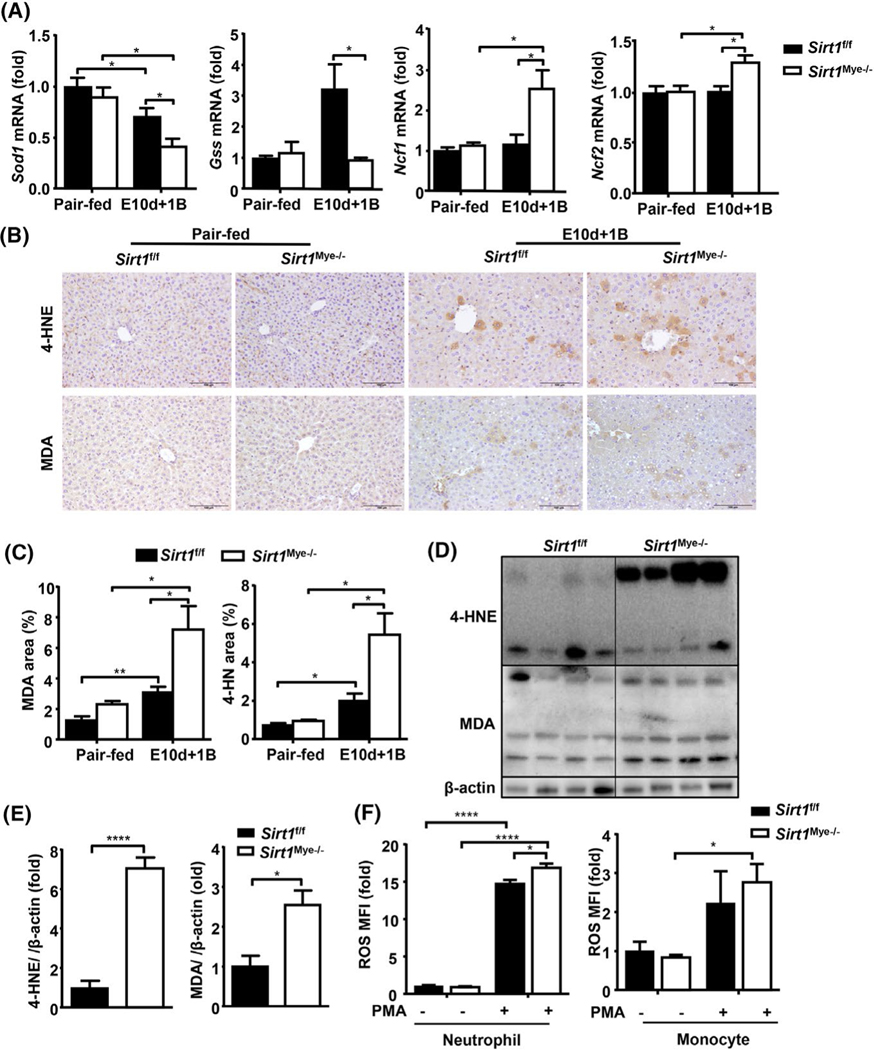
FIGURE 2.
Sirt1Mye−/− mice are more susceptible to chronic-plus-binge ethanol-induced oxidative stress and inflammation in the liver. Sirt1Mye−/− (n = 7) and Sirt1f/f (n = 9) mice were subjected to E10d+1B or pair feeding. Mice were euthanized 9 h after gavage. Liver samples were collected and analyzed. (A) RT-qPCR analysis of reactive oxgen species (ROS)-related genes. (B,C) Liver tissues were subjected to immunostaining with an anti-malonaldehyde (MDA) or anti-4-HNE antibody. Representative images are shown in panel B. Relative staining is quantified and shown in panel C. (D,E) Western blot analyses of 4-HNE and MDA, and their quantitation results are shown in panel E. (F) BM neutrophils from Sirt1Mye−/− and Sirt1f/f were isolated and stimulated with or without phorbol 12-myristate 13-acetate (PMA). The ROS levels were measured by flow cytometric analyses. The ROS levels are calculated and shown. MFI relative fluorescence unit. Values represent means ± SEM. *p < 0.05; **p < 0.01; ****p < 0.0001