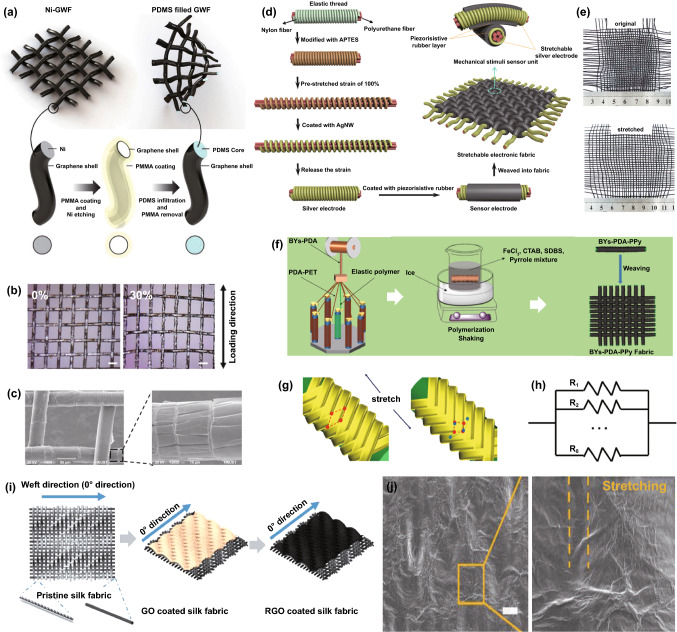
Fig. 7.
a A woven-structure strain sensor by depositing graphene on a nickel mesh and replacing the nickel by PDMS, b the surface morphologies of the sensor under 0 and 30% strain respectively, and c the crack formation with applied strain to illustrate the sensing mechanism [176]. Copyright © 2019 American Chemical Society. d Illustration of a woven strain sensor through weaving Ag NWs and piezoresistive rubber-coated yarns into a fabric, and e the images of the fabric sensors in the original and stretching state [185]. Copyright © 2016 Wiley–VCH. f Fabrication of a strain sensor by weaving conductive polymer-modified yarn into a plain fabric, g the illustration of the yarn without and with stretching, and h the resistance model of the sensor showing the sensing mechanism [175]. Copyright © 2019 American Chemical Society. i The process of coating graphene on the surface on a woven silk fabric as a strain sensor, and j crack formation on the graphene layer to show the mechanism of the sensor [177]. Copyright © 2020 Wiley–VCH