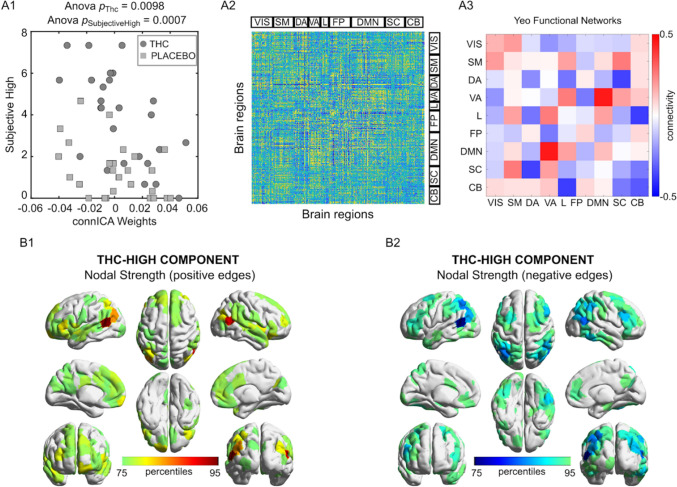
Figure 4.
THC induced feeling of subjective high connICA component. (A1) Drug differences in the individual subject weights associated with the connICA component (anova test, p < 0.01 Bonferroni corrected across the 20 robust components, see “Methods”) in association to subjective high in each drug condition (circles, THC; squares, placebo). The connICA component and subjective high ratings are strongly correlated (see “Methods” for details). (A2) The functional connectivity component extracted by connICA. Pairwise associations between brain regions are ordered by resting-state functional networks as proposed by Yeo et al.52. (A3) For clarity, the same component, depicted after averaging across functional networks, shows prominent connectivity within the DMN and attentional areas. (B1,B2) Nodal strength (sum over columns of (A2), including only: (B1) positive edges or (B2) negative edges) of the top 25% regions involved in the identified THC-differentiating component.