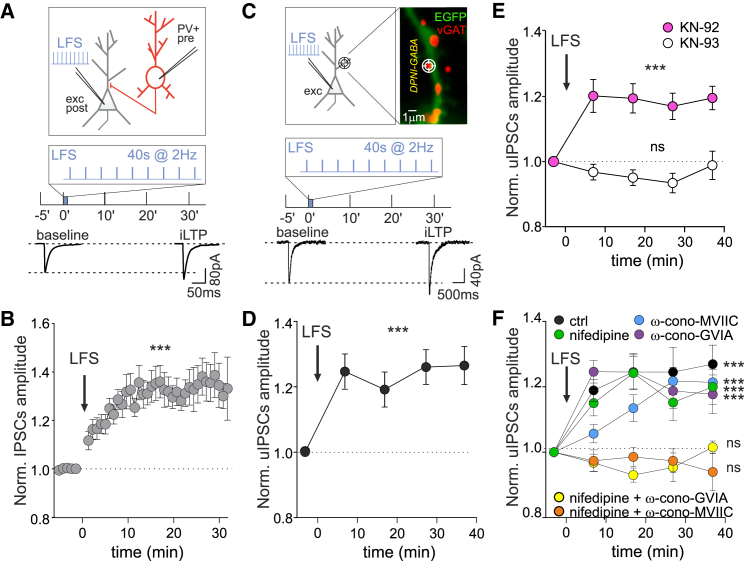
Figure 1.
LFS induces iLTP at GABAergic synapses
(A) Top: Experimental configuration of paired-patch recordings including an electrically stimulated presynaptic parvalbumin-tdTomato positive (PV+) interneuron (red) and a postsynaptic excitatory hippocampal neuron (gray) receiving the low-frequency protocol (LFS, 2-Hz APs train for 40 s). Bottom: Representative averaged inhibitory postsynaptic currents (IPSCs)—driven by the PV+ interneuron activation—elicited before and 30 min after the LFS, as schematized above.
(B) Potentiation of IPSC amplitude (iLTP) after LFS (arrow; n = 33 neurons, F38,875 = 5.9, p < 0.001, one-way ANOVA followed by Tukey's multiple comparison test).
(C) Top: Experimental configuration including an excitatory hippocampal neuron (gray) receiving the LFS. The “target” symbol indicates an individual GABAergic synapse where DPNI-GABA was uncaged (see STAR Methods). Inset: Representative dendritic portion of a neuron expressing EGFP (green), with GABAergic synapses identified by live labeling of vGAT (red, see STAR Methods). Scale bar, 1 μm. Bottom: Representative averaged traces of uIPSCs before (baseline) and 30 min after LFS (iLTP) as schematized above.
(D) uIPSCs are potentiated after LFS (n = 30 synapses from nine neurons; F4,120 = 6.3, p < 0.001; one-way ANOVA followed by Tukey's multiple comparison test).
(E) CaMKII is required for LFS-induced iLTP. uIPSC amplitude normalized to baseline values in the presence of KN-93 (white; n = 19 synapses from five neurons; F4,64 = 1.6, p > 0.05, one-way ANOVA followed by Tukey's post-test) and the inactive analog KN-92 (pink; n = 26 synapses from seven neurons; F4,92 = 6.5, p < 0.001; one-way ANOVA followed by Tukey's post-test).
(F) Influence of voltage-gated calcium channels (VGCCs) on iLTP expression. Relative (after/before) uIPSC amplitude upon LFS in control conditions (black; n = 46 synapses from 14 neurons; F4,144 = 10.2, p < 0.001), or in the presence of the following VGCCs blockers: ω-conotoxin MVIIC for P/Q and N-type (blue; n = 16 synapses from four neurons; F4,64 = 9.1, p < 0.001), or nifedipine for L-type (green; n = 35 synapses from nine neurons; F4,120 = 5.8, p < 0.001) or ω-conotoxin GVIA for N-type (purple; n = 69 synapses from 16 neurons; F4, 205 = 11.5, p < 0.001) or nifedipine and ω-conotoxin MVIIC (orange; n = 24 synapses from six neurons; F4,80 = 0.3, p > 0.05) or nifedipine and ω-conotoxin GVIA (yellow; n = 17 synapses from six neurons; F4,52 = 1.9, p > 0.05). All statistical comparisons were performed with one-way ANOVA followed by Tukey's multiple comparison test. Values are expressed as mean ± SEM. ∗∗p < 0.01, ∗∗∗p < 0.001, ns = not significant. See also Figure S1.