Figure 1.
Oral pterostilbene enters circulation but bioavailability to muscle is low
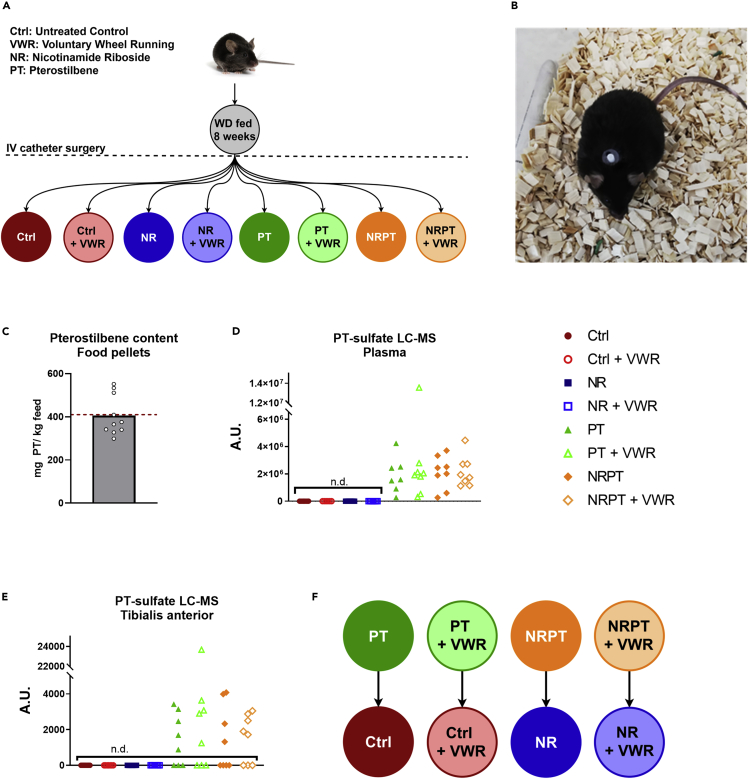
(A) Schematic overview of the group setup. C57BL/6NTac mice were fed a WD for 8 weeks, then underwent surgery with the insertion of a jugular catheter connected to a vascular access button. After recovery, the mice were split into eight groups, creating a full-factorial experiment setup with the three factors; nicotinamide riboside (NR), pterostilbene (PT), and voluntary wheel running (VWR). Blue and orange groups received NR (100 mg/kg/day), green and orange groups received PT (410 mg pr. Kg diet), and hollow groups had access to VWR.
(B) Top-down picture of C57BL/6NTac mouse with a Vascular Access Button for the facilitation of intravenous NR administration.
(C) PT content in food pellets. 10 food pellets were randomly selected and tested for PT content. The dotted red line shows the expected amount of PT. Data are presented as mean with overlain data points.
(D) Relative amounts of PT-sulfate in plasma as measured by LC-MS. Samples, where PT-sulfate could not be detected, have been marked with n.d.
(E) Relative amounts of PT-sulfate in TA muscle as measured by LC-MS and normalized to tissue mass. Samples, where PT-sulfate could not be detected, have been marked with n.d.
(F) Schematic representation of the merging of PT groups into their respective control groups.