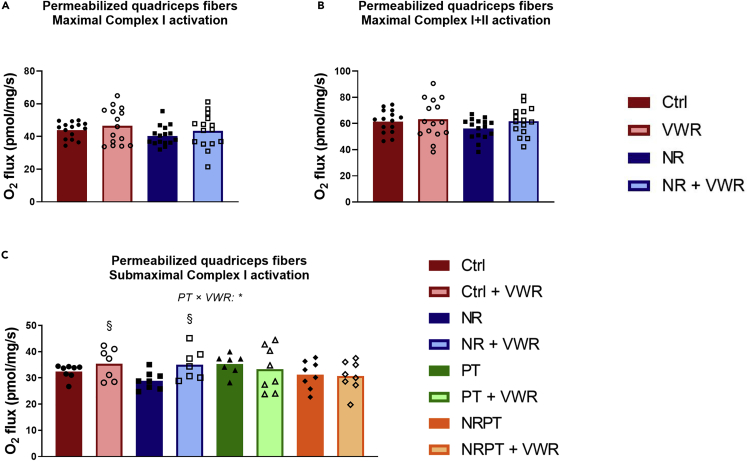
Figure 5.
Neither NR nor VWR increases maximal respiratory capacity in permeabilized muscle fibers.
Oxygen consumption of permeabilized muscle fibers from the superficial lateral part of quadriceps muscle
(A) Incubated in the presence of pyruvate, malate, glutamate, and saturating levels of ADP (5 mM), leading to the maximal activation of Complex I.
(B) Incubated in the presence of pyruvate, malate, glutamate, saturating levels of ADP and succinate, leading to the maximal activation of Complex I and Complex II.
(C) Incubated in the presence of pyruvate, malate, glutamate, and subsaturating levels of ADP (0.1 mM), leading to the submaximal activation of Complex I.
All data were corrected for residual oxygen consumption and are presented as mean with overlain data points. Two-way ANOVA was performed for (A) and (B). Three-way ANOVA was performed for (C), and Tukey’s test was employed to explore the interaction. Statistical significance was indicated in the following manner: Effects of VWR: p < 0.05 = §. Interactions are written out in the figure and noted with: p < 0.05 = ∗. The symbols indicate a simple effect of VWR within groups that did not receive PT. See also Figure S4.