Figure 3. Gastrointestinal stem cell niche.
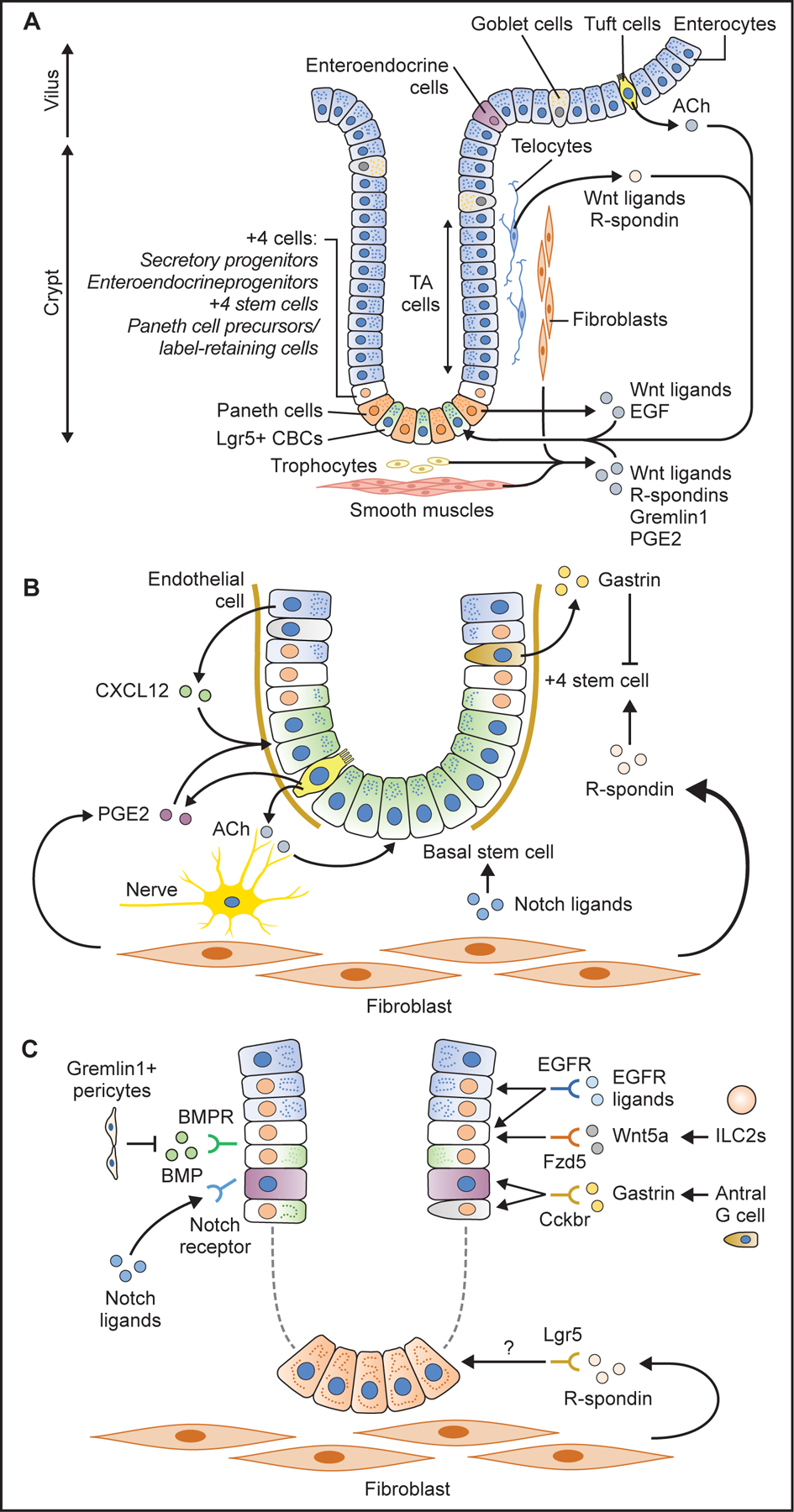
(A) Schema of intestinal stem cells and their niche. Lgr5+ CBCs at the base and +4 stem/progenitor cells are supported by surrounding stromal cells which secrete numerous niche factors such as R-spondins, Wnt ligands, Gremlin1, epidermal growth factor (EGF), prostagrandin E2 (PGE2). Epithelial tuft cells play a role by producing acetylcholine (ACh). (B) Antral stem cell niche factors. R-spondin 3 from stromal myofibroblasts activates +4 stem cells. Gastrin produced from G cells suppress +4 stem cell activity via CCK2R receptor. Notch ligands, ACh from nerves and tuft cells, PGE2 from tuft cells, as well as CXCL12 from endothelial cells promote stem cell expansion and contribute to cancer development. (C) Corpus stem cell niche factors. Isthmus stem cells and progenitors are supported and activated by specific niche factors such as Notch ligands, Wnt5a, gastrin, and EGFR ligands through their corresponding receptors.
